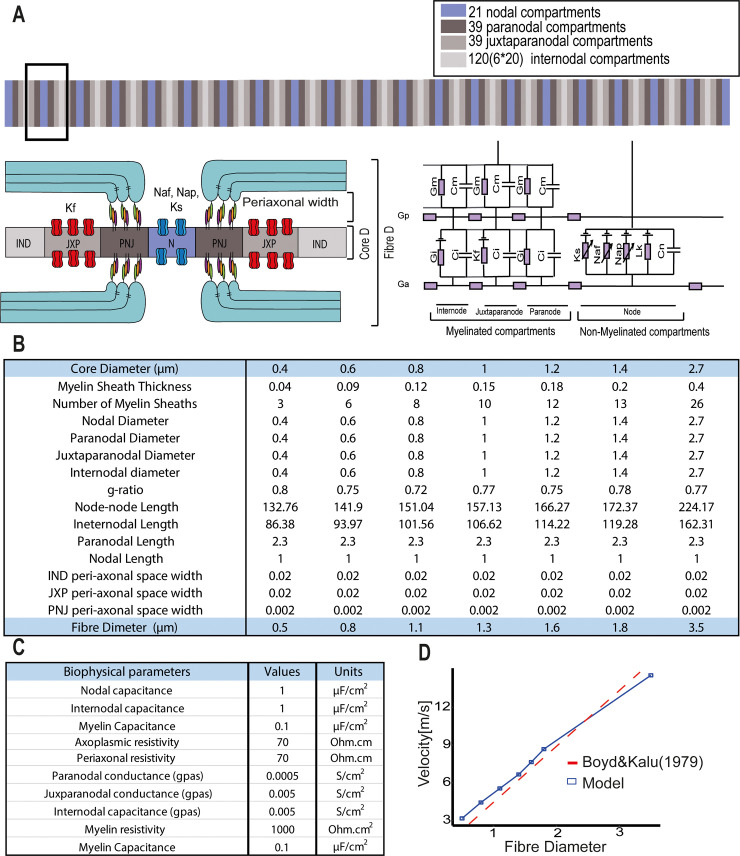
Fig 7. Structural and biophysical parameters used to simulate a 21 node myelinated axon.
(A) A double cable circuit of the model to represent the axolemma (Ga), the peri-axonal space (Gp), and the myelin sheath (Gm) was generated with the simulator NEURON. Specifically, 21 nodal, 39 paranodal, 39 juxtaparanodal, and 20 internodal compartments were created. (B) Anatomical parameters used in the model. Seven diameters were chosen from CNS measurements from macaque EM studies [42], the number of myelin lamella (nl) was calculated from the myelin periodicity value of 0.0156 μm [71], the node-to-node length was taken from the linear relationship measured from rat nerve fibres [72], the juxtaparanodal length was extrapolated from the diameter-dependent scaling relationship from the ventral root of cats [73], and the paranodal length was determined from the average value of Caspr1 staining measured from our non-neurological control cases. (C) Biophysical parameters. Axon capacitance was based on data from rat ventral roots [86], myelin capacitance and leak conductance per lamella were based on the frog sciatic nerves [87]. The resistivity was set to 1,000 Ohm * cm2 for each myelin lamella [40,87,88,89,90,91]. (D) Plot showing the conduction velocity of the model across the 7 fibre diameters simulated (blue) and the velocity data measured in cat hind limb nerves [43].