Figure. 2. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB).
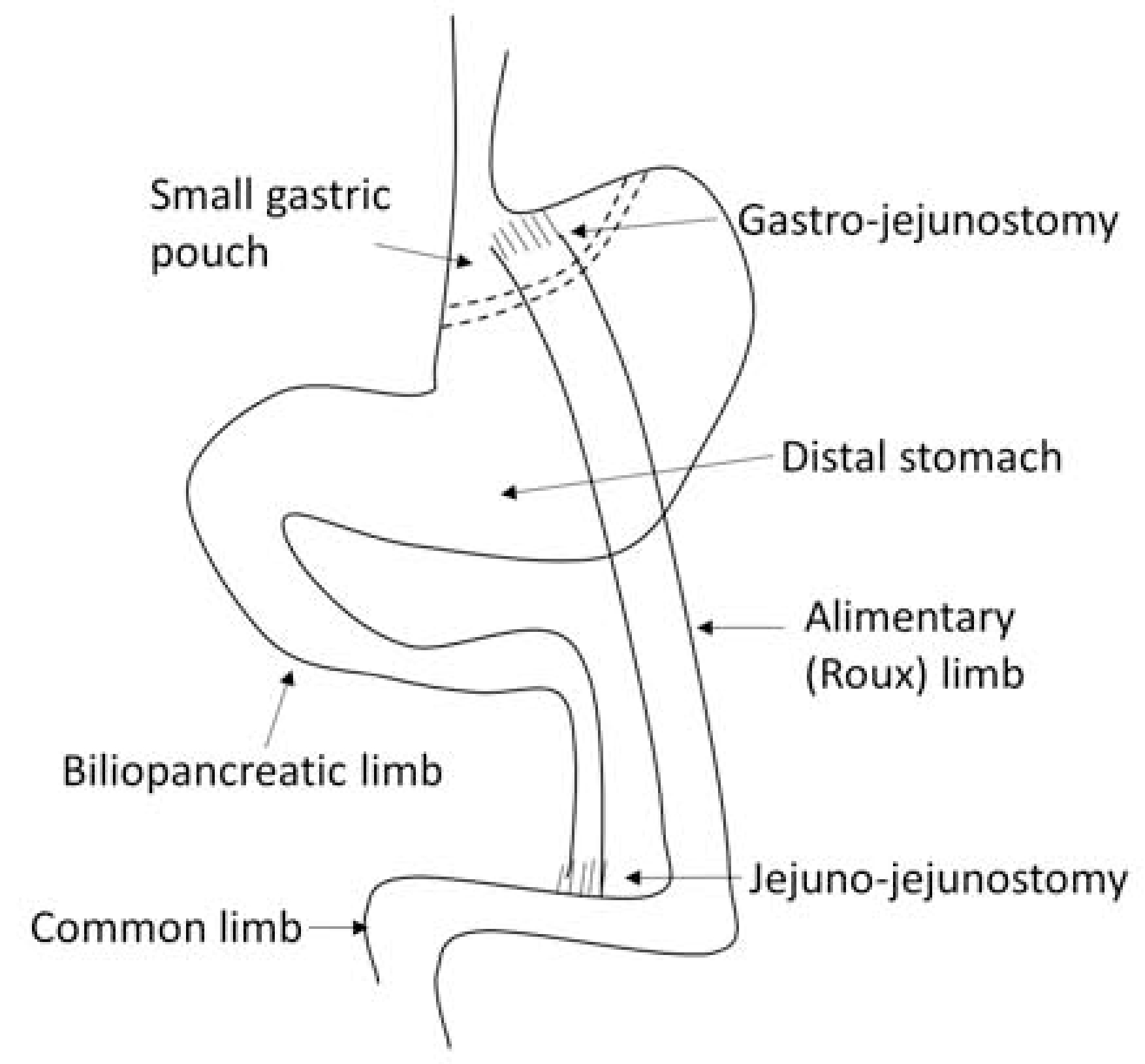
Schematic diagram of RYGB. The stomach is divided into a small gastric pouch and a distal stomach along the dotted lines. The jejunum is transected and the distal part is connected to the gastric pouch through a gastro-jejunostomy, which creates a Roux limb or alimentary limb, as indicated. The continuity of the gastrointestinal tract is re-established by connecting biliopancreatic limb to the jejunum through a jejunojejunostomy. The small intestine distal to the jejuno-jejunostomy is called common limb. RYGB leads ingested food to bypass the distal stomach, duodenum and proximal jejunum, and rapidly go through the small gastric pouch and flow into the jejunum. Therefore, nutrients are present in the Roux limb without bile, whereas bile and pancreatic secretions are present in the biliopancreatic limb, but no nutrients. Nutrients are mixed with bile and pancreatic secretions in the common limb.
