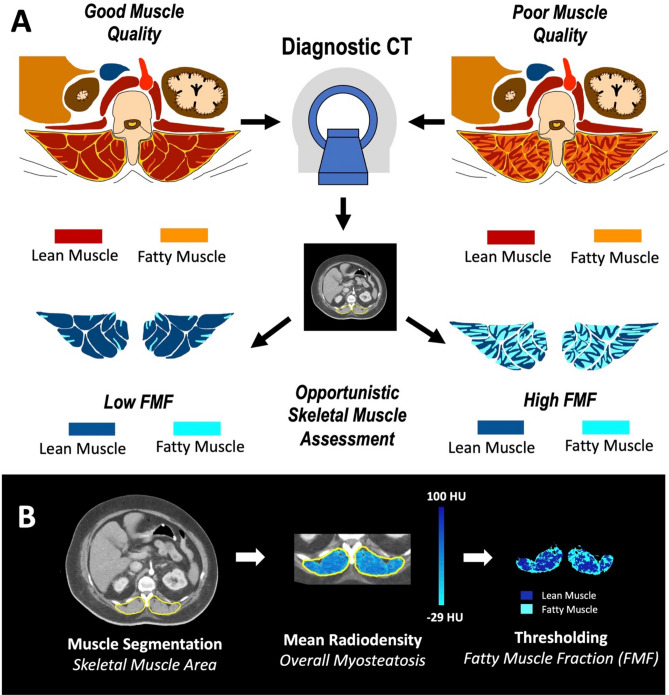
Figure 2.
The concept of FMF. (A) Skeletal muscle fat infiltration is considered an indicator of muscle quality. Based on densitometric thresholds and accepted cut-off values of lean and fatty skeletal muscle, muscle compartments may be separated into areas of fatty and lean muscle. The FMF is calculated as the area of fatty muscle tissue related to the total skeletal muscle area, resulting in a relative and comparable measure of muscle quality. This biomarker can be opportunistically obtained from clinical CT scans. (B) Skeletal muscle area was obtained as the bilateral compartment area of paraspinal skeletal muscles at the level of the superior mesenteric artery. Within the skeletal muscle area, muscle tissue is identified by an attenuation threshold range of 100 to − 29 HU. Mean Radiodensity was highlighted to visualize overall muscle fat infiltration (myosteatosis). Based on thresholds ranges of − 29 to 29 HU for fatty muscle and 30 to 100 HU for lean muscle, FMF was calculated. CT Computed tomography, FMF Fatty muscle fraction, HU Hounsfield units.