Figure 4.
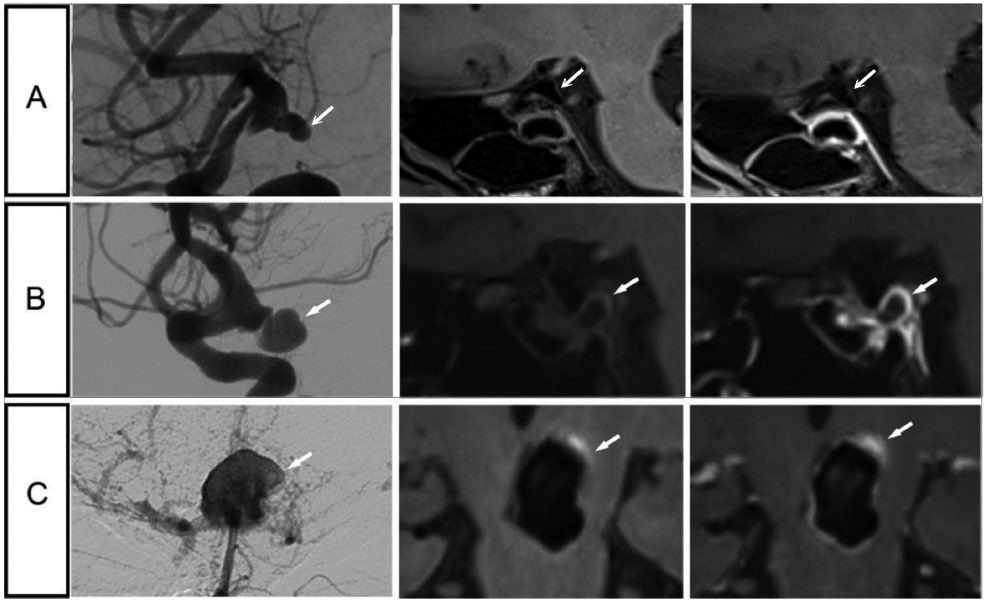
Representative cases of patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic intracranial aneurysms. A, Images of a 52-year-old man with an asymptomatic aneurysm at the right internal carotid artery terminal, measuring 3.8mm. B, Images of a 64-year-old woman with oculomotor nerve palsy and an aneurysm at the right internal carotid artery terminal, measuring 9.3mm. C, Images of a 51-year-old man with sentinel headache and an aneurysm at the top of basilar artery, measuring 16mm. Aneurysm wall hyper intensity is present prior to contrast administration, which is uncommon in the current cohort (9 aneurysms in the whole dataset). Potential explanation might be micro bleeding, which may be related to sentinel headache. For each aneurysm represented on a row, a digital subtraction angiography image is shown in the left column, a vessel wall image is in the middle column, and a post-contrast vessel wall image is shown in the right column.
