Fig.2. inhibition overcomes tumor resistance to anti-PD1 therapy.
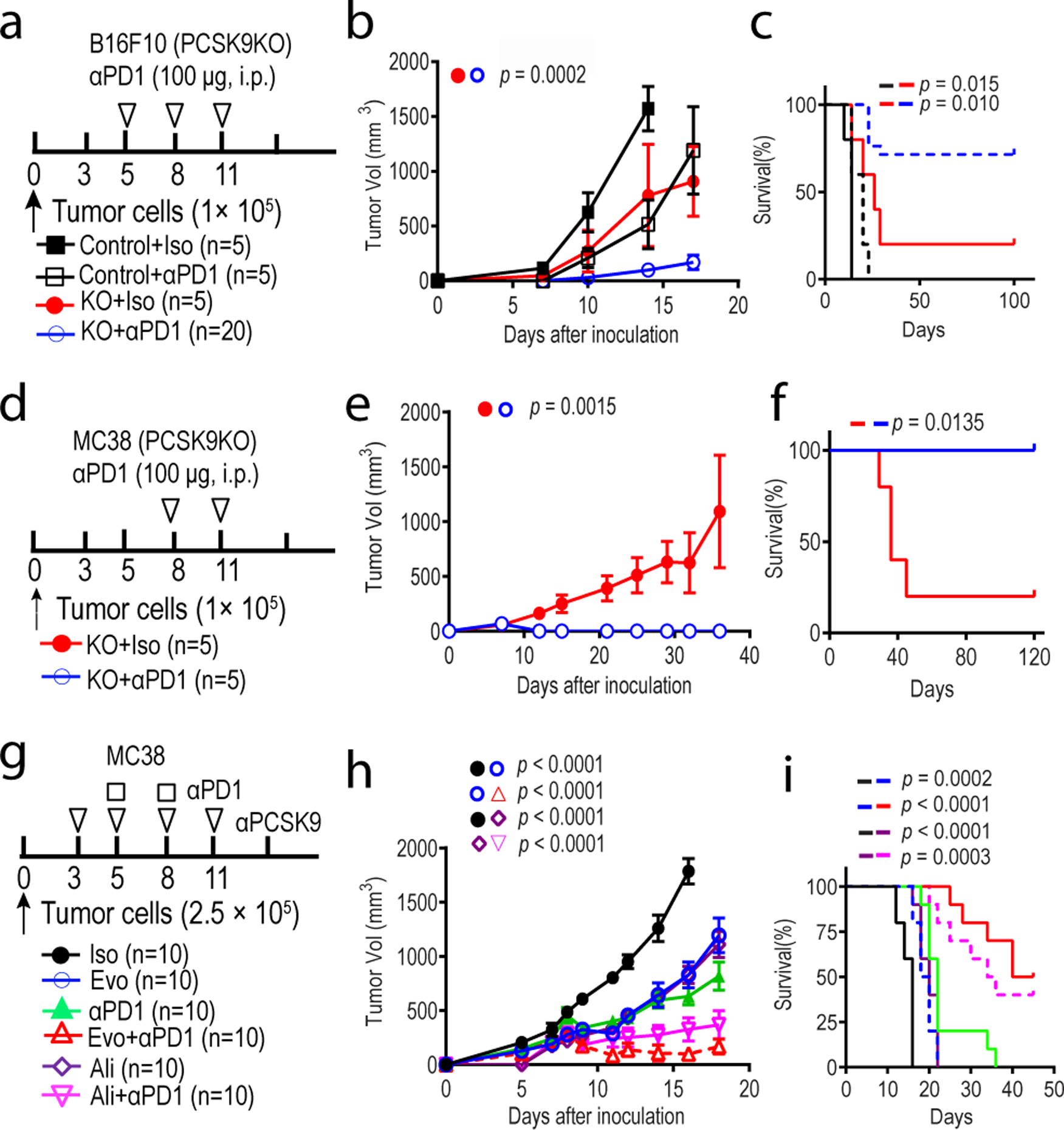
a-c. Treatment of vector control and PCSK9 knockout B16F10 melanoma with an anti-PD1 antibody in syngeneic mice. Experimental protocol (a), tumor growth curve (b), and overall survival (c) were shown. n=5, 5, 5, and 20 mice in the four groups, respectively. d-f. Treatment of vector control and PCSK9KO MC38 colon cancer with an anti-PD1 antibody in syngeneic mice. Experimental protocol (d), tumor growth curve (e), as well as overall survival (f) were shown. n=5 mice per group. g-i. Treatment of MC38 colon cancer with combined anti-PCSK9 (evolocumab, Evo; or alirocumab, Ali) and anti-PD1 antibodies in mice. Experimental protocol (g), tumor growth curve (h), as well as overall survival (i) were shown. n=10 mice per group. Shown were combined results from two separate experiments. Error bars represent mean ± S.E.M. P values were calculated by two-way ANOVA in b, e, h and logrank test in c, f, i, respectively.
