Figure 3 – I-F3b Tn6900 element derived from A. salmonicida S44 allows RNA-guided transposition with typical and atypical repeats.
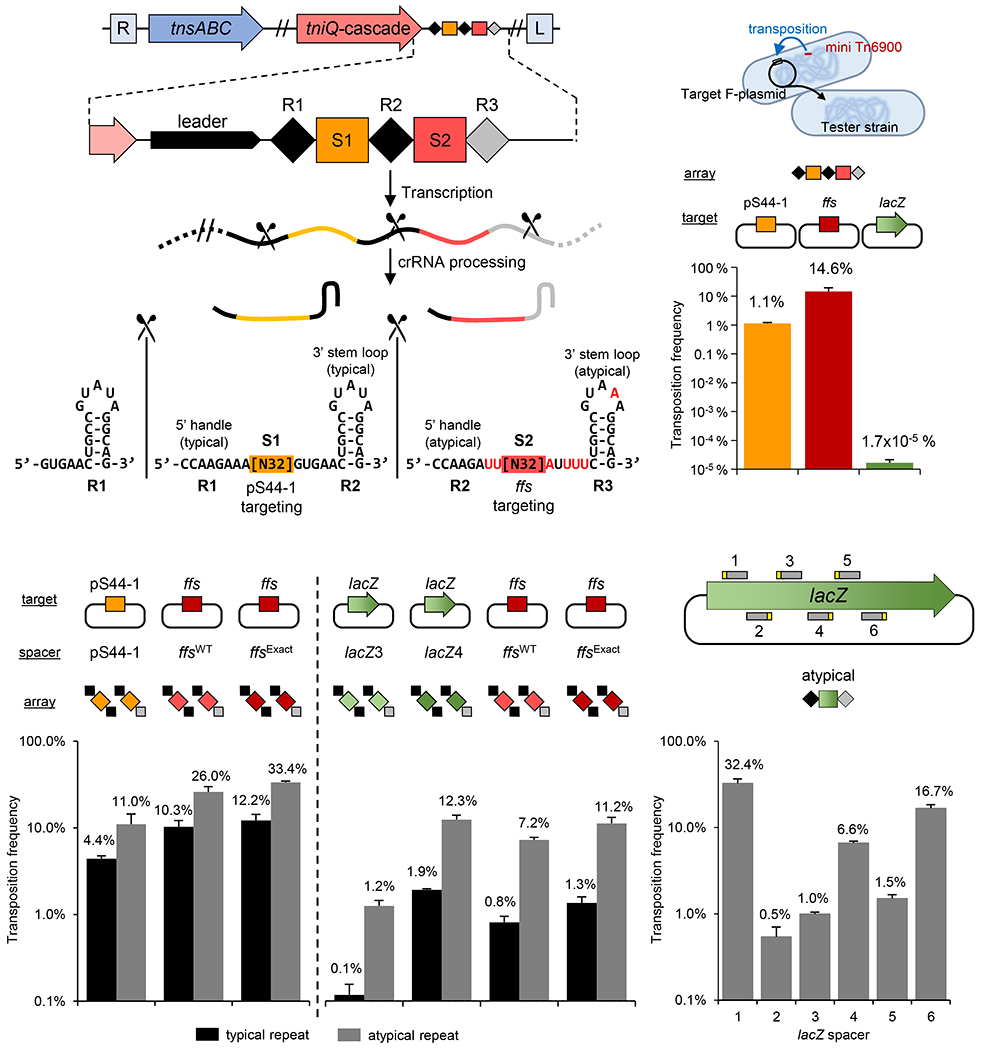
Various transposition targets were tested using the A. salmonicida S44 native array or as individual repeat-spacer-repeat units. (a) Simplified representation of transposition/CRISPR-associated genes, CRISPR array (marked as in Figure 1) and the resulting typical and atypical guide RNAs with the 5’ and 3’ handles indicated. Position of Cas6 processing is indicated (scissors). (b) Frequency of transposition found with the native A. salmonicida S44 array with targets constructed into an F plasmid; A. salmonicida S44 plasmid pS44-1 (pS44-1), chromosomal ffs att site (ffs) or a negative control, lacZ gene. (lacZ) (c-e) Transposition frequency found with a single repeat-spacer-repeat unit in various combinations of spacers with typical or atypical repeats from Tn6900 with the indicated targets constructed into an F plasmid. All data indicate mean +/− standard deviation (n=3).
