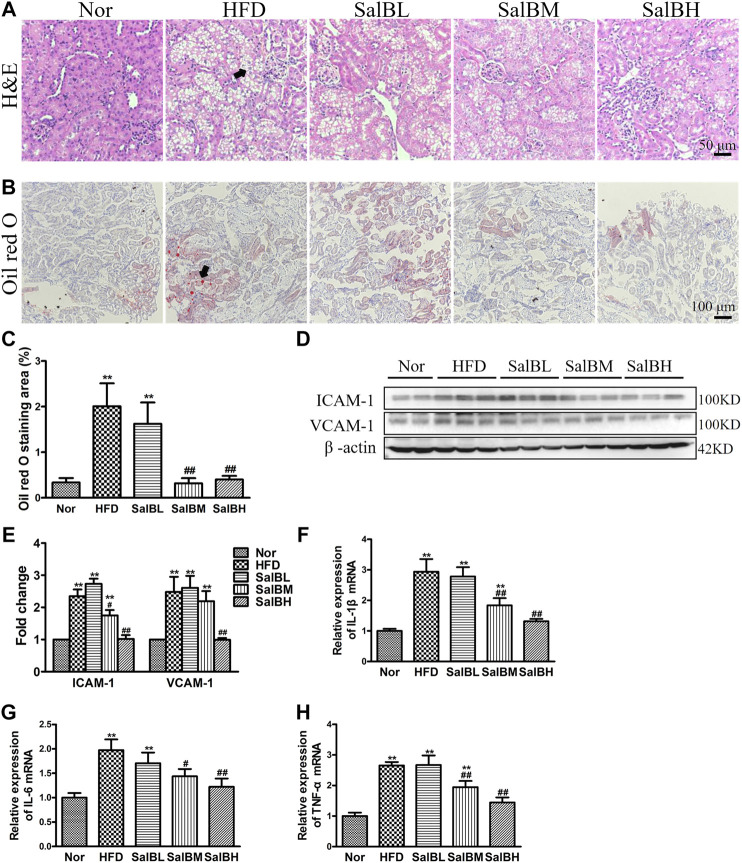
FIGURE 1.
SalB inhibited tubular injury in the kidneys of HFD mice (A) H&E staining illustrated vacuolated proximal convoluted tubular cells (arrowheads) in HFD mice were attenuated by SalB treatment (magnification ×400) (B) The kidney lipid content in the mice was observed using oil red O staining (arrowheads) (magnification ×200). HFD was associated with increased lipid deposition in the kidney of the mice, which was ameliorated with SalB treatment (C) Quantitative analysis of Oil red O staining (D,E) Western blotting showed increased ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in the kidney cortex of the HFD mice was ameliorated with SalB treatment. The corresponding quantifications were shown as well (F,G,H) Analysis of renal mRNA expression levels by quantitative real-time PCR for IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in HFD-fed mice with or without SalB treatment. Nor, mice fed with normal diet; HFD, mice fed with high-fat diet; SalBL, SalBM, or SalBH, mice fed with high-fat diet and treated with low dosage of SalB (3 mg/kg), medium dosage of SalB (6.25 mg/kg), or high dosage of SalB (12.5 mg/kg), respectively. Data are represented as means ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, compared with Nor; # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01, compared with HFD.