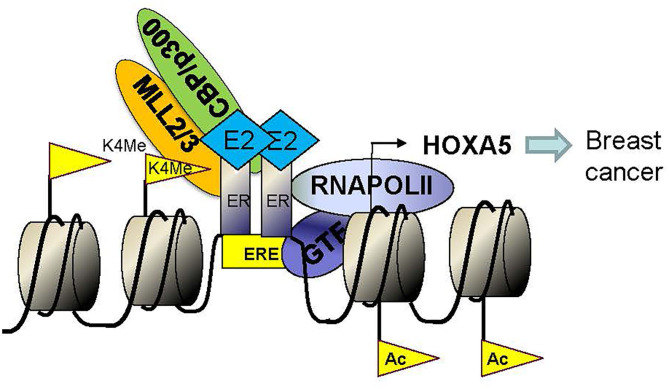
Figure 8.
Model showing the mechanism of E2-mediated activation of HOXA5. Binding of E2 induces conformational change in ERs and induces dimerization and activation of ERs. Activated ER dimers enter the nucleus, bind to the HOXA5 promoter (EREs). ER co-regulators (CBP, p300, MLL2, MLL3, and others) also bind to the HOXA5 promoter, modify chromatins (H3K4-trimethylation via MLL2 and MLL3 and histone acetylation via CBP/p300), aid in recruitment of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) and general transcription factors (GTFs) to the promoter and ultimately lead to transcription activation of HOXA5.