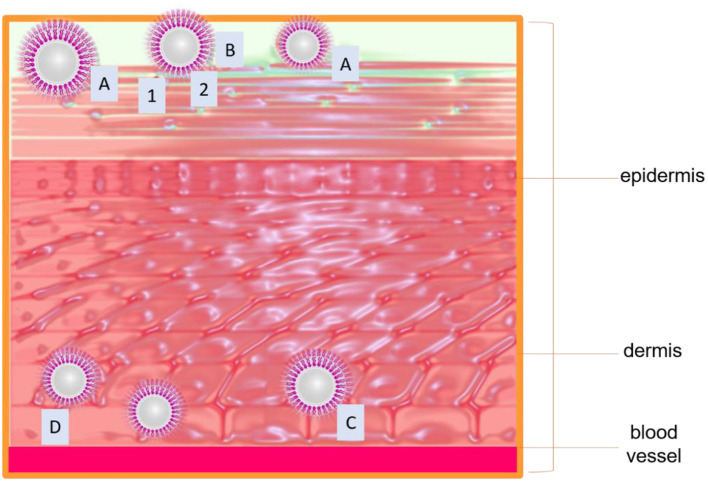
Figure 6.
(A) Adsorption of liposomes to the skin surface; drug transfer from liposomes to skin. (B) Rupture of vesicles, the release of content, and the penetration of the free molecules into the skin via intracellular (1) or intercellular route (2). (C) Penetration of unilamellar vesicles via the lipid-rich channels to the dermis where they slowly release their content due to disruption or degradation of liposomal membranes. (D) Penetration of multilamellar vesicles via the lipid-rich channels. On the route of penetration of multilamellar vesicle can lose one or more outer lipid lamellae which would lead to partial release of the encapsulated material.