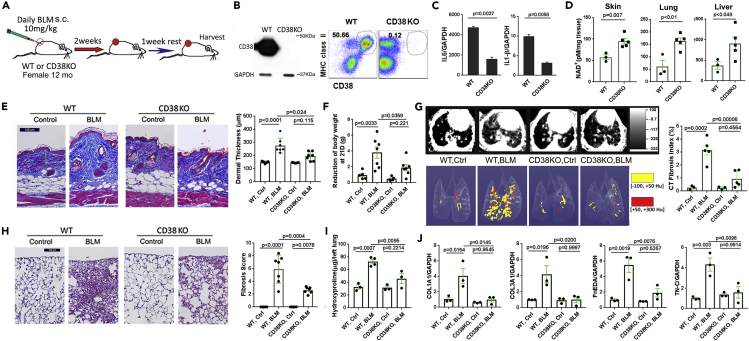
Figure 2.
Deletion of CD38 ameliorated skin and lung fibrosis
(A) Schematic of experimental design. Twelve-month-old female CD38-null mice or wild-type control mice on standard chow received daily s.c. bleomycin (BLM) injections (10 mg/kg) for 14 d. After 21 d, mice were sacrificed. Five to 7 mice were used for each group, and experiments were repeated 2 times.
(B) CD38 expression undetectable in inguinal lymph nodes (representative immunoblot) and spleen cells (flow cytometry) in CD38-null mice.
(C) Reduced cytokine gene expression (qPCR) in CD38-null bone-marrow-derived M1 macrophages.
(D) Elevated NAD+ levels in skin, lungs, and liver in CD38-null mice.
(E) Attenuated increase in dermal thickness (representative images, trichrome stain; scale bar represents 100 μm) and collagen deposition in CD38-null mice. Results are means ± SEM (standard error of the mean) from an experiment representative of two independent experiments.
(F) Bleomycin treatment-induced weight loss is mitigated in CD38-null mice (n = 5–7 mice/per group).
(G–J) Lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin is attenuated in CD38-null mice. (G) microCT of the lungs (n = 5 mice/group). Representative cross-sectional and 3D images (left) and quantitative lung fibrosis index (right). (H) Lung histology (trichrome stain, scale bar represents 100 μm); representative images (left) and measurement of lung fibrosis (right). (I and J) Collagen accumulation and fibrotic gene expression in the lungs. Error bars in all graphs, means ± SEM.