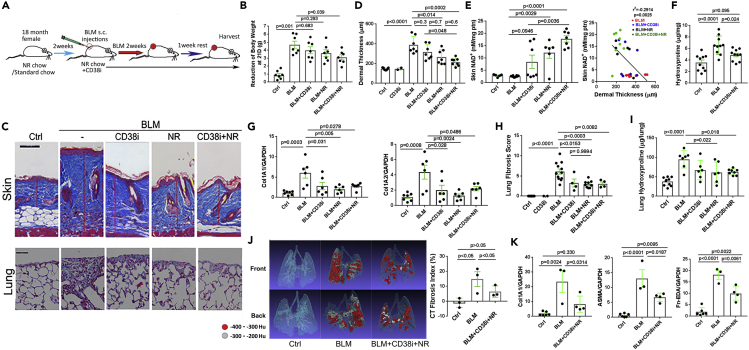
Figure 3.
NAD+ boosting ameliorated skin and lung fibrosis in aged mice
(A) Schematic of experimental design. Eighteen-month-old female C57/BL6 mice maintained on standard chow or NAD precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR)-supplemented chow diet. Mice received daily s.c. bleomycin (BLM) injections for 14 d alone or combined with CD38 inhibitor 78c administered by oral gavage. At 21 d, mice were sacrificed and skin and lungs were harvested for analysis. Results from three independent experiments with 6–8 mice per group.
(B–D) NAD+ boosting attenuated bleomycin-induced (B) body weight loss, and (C and D) increase in dermal thickness (representative images, trichrome stain; scale bars represent 100 μm). Results are means ± SEM (standard error of the mean) from an experiment representative of three independent experiments.
(E) NAD+ levels in the skin; results are means ± SEM; negative correlation (Pearson's) of skin NAD+ levels with dermal thickness.
(F–H) (F and G) Skin collagen content (hydroxyproline assays); and gene expression (qPCR); (C) (H) Lung fibrosis quantification (modified Ashcroft score).
(I) Lung collagen content.
(J) Lung fibrosis imaging, representative microCT images (left) and fibrosis quantitation (right).
(K) mRNA levels in the lung determined by qPCR; results are means ± SEM.