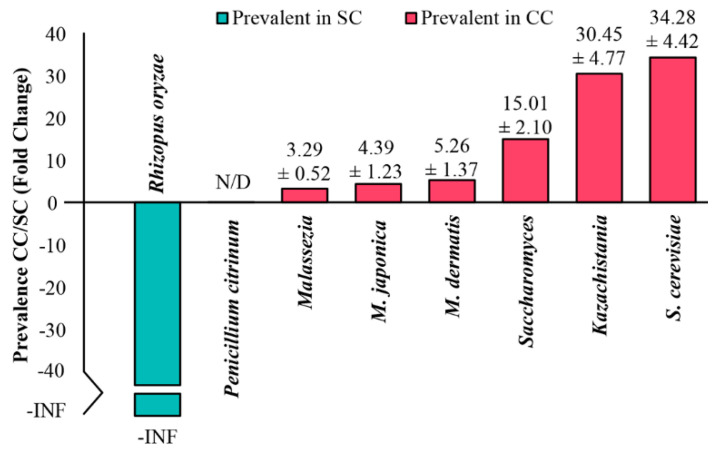
Figure 5.
Relative quantification of different microorganisms in stool samples from SC and CC animals by qPCR. Equimolar samples of DNA extracted from stool samples obtained from each mouse were consolidated into two pools, representing SC and CC groups. Samples from these pools were then used in qPCR experiments, with primers previously described in the literature as specific to Saccharomyces, Kazachstania, and Malassezia genera, as well as to the species Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Malassezia dermatis, Malassezia japonica, Rhizopus oryzae, and Penicillium citrinum. The Ct values obtained for each of these taxa were normalized by the Ct obtained after amplifying the pooled DNAs with the primer pair used to amplify the fungal ITS1 amplicons. Next, the normalized Cts were used to calculate the relative prevalence of each genus/species in the CC pool, in relation to the SC pool (CC/SC). The relative quantification values for each taxon (Fold Change) are shown in the graph, as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments (each performed in triplicate). The species Rhizopus oryzae was detected only in the DNA pool from SC animals, so its CC/SC ratio is represented in the graph as negative, to infinity (-INF). The species Penicillium citrinum was not detected (N/D) in any of the experiments, with either DNA pool.