Figure 2.
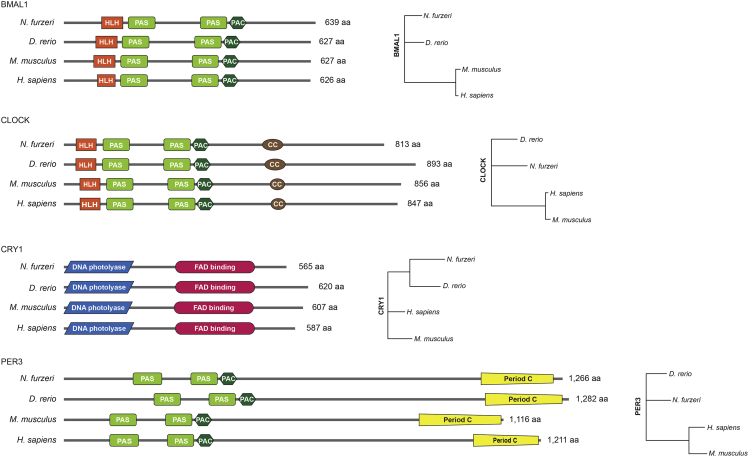
Core circadian clock components are highly conserved in the turquoise killifish
The functional domains of the core clock proteins in four species, Nothobranchius furzeri (turquoise killifish), Danio rerio (zebrafish), Mus musculus (mouse), and Homo sapiens (human) are shown on the left. Translated amino acid sequences of turquoise killifish, zebrafish, mice, and human BMAL1 (XM_015965280 [bmal1], NM_131577 [bmal1a], NM_007489, and NM_001030272, respectively), CLOCK (XM_015971720 [clockb], BC163244 [clock1], AF000998, and AF011568, respectively), CRY1 (XM_015964931 [cry1b], NM_001077297 [cry1aa], NM_007771, and NM_004075, respectively) and PER3 (XM_015959552 [per3], AF254792, NM_011065, and NM_001289862, respectively) were used for the analysis. The phylogenetic trees (right) were constructed using neighbor-joining clustering.
See also Figure S2.