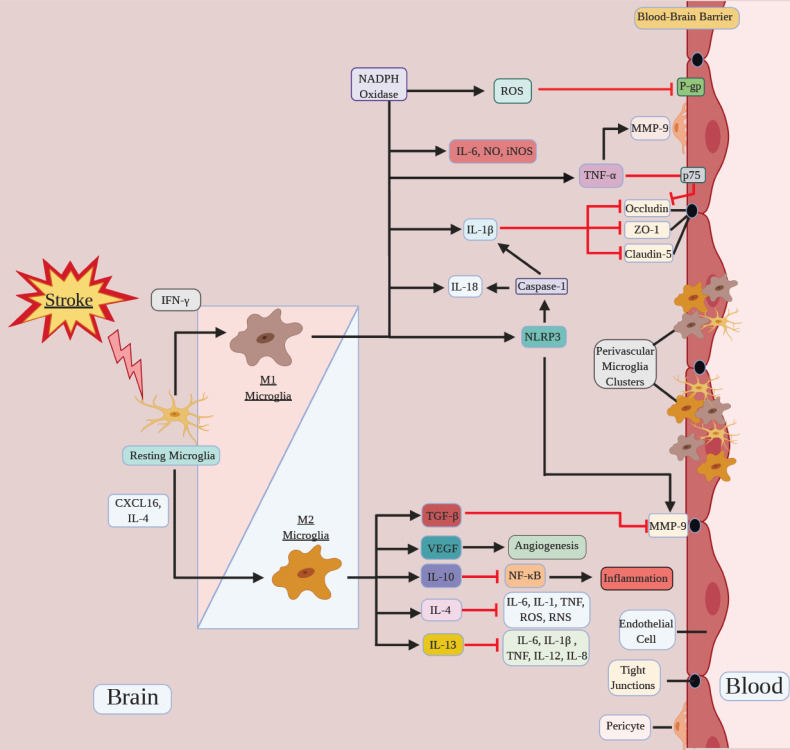
Fig. (1).
Microglia polarization directs BBB function after stroke. Microglia polarize to a spectrum of pro-inflammatory M1/ anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype in response to stroke. M1 microglia promote ROS production, NLRP3 activation and pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion, such as IL-6, NO, iNOS, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-18, which aggravate BBB disruption. M2 microglia release growth and trophic factors such as VEGF and anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-13, IL-10, and TGF-β, which facilitate the repair, or inhibit BBB damage. Microglia can also aggregate at the perivascular space to directly interact with the BBB and affect the BBB permeability. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).