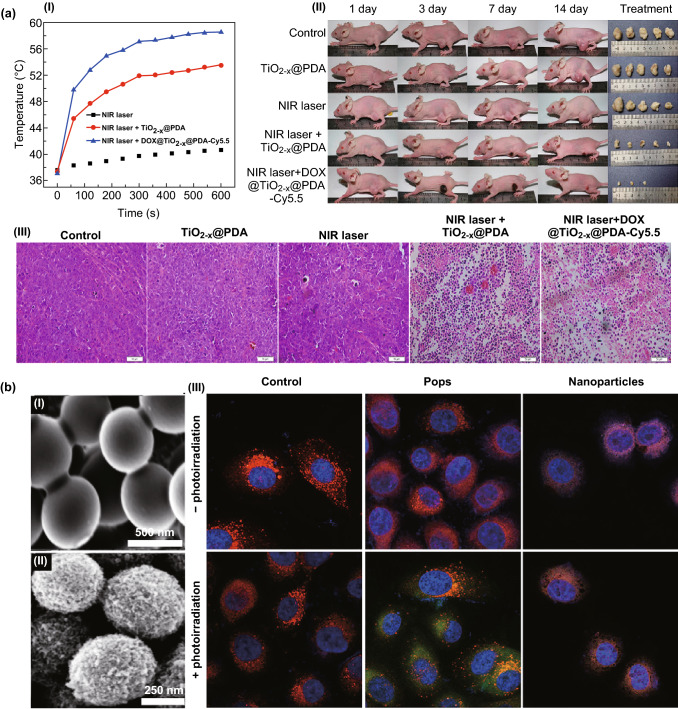
Fig. 7.
a Black TiO2 nanocarriers employed for a chemo/photodynamic/photothermal therapy in vivo. The efficient temperature raise (a-I) caused by black TiO2 nanocarriers (DOX@TiO2−x@PDA-Cy5.5) under NIR irradiation (808 nm, 1.0 W cm−2) triggers (a-II) a tumor growth inhibition. (a-III) Histological sections of the treated tumors indicate a noticeable cellular necrosis and apoptosis. Adapted from Ref. [47] with permission from the American Chemical Society. b Upon on/off-switchable photoactivation, TiO2 pops generate high-turnover, flash intracellular ROS. SEM images of mesoporous TiO2 Pops (b-I) before and (b-II) after solvothermal treatment. (b-III) The intracellular ROS generation using pops and smooth nanoparticles in the presence (+) and absence (−) of the irradiation. The green, red, and blue colors represent the intracellular ROS, mitochondria, and nucleus, respectively.
Adapted from Ref. [15] with permission from the Springer Nature. (Color figure online)