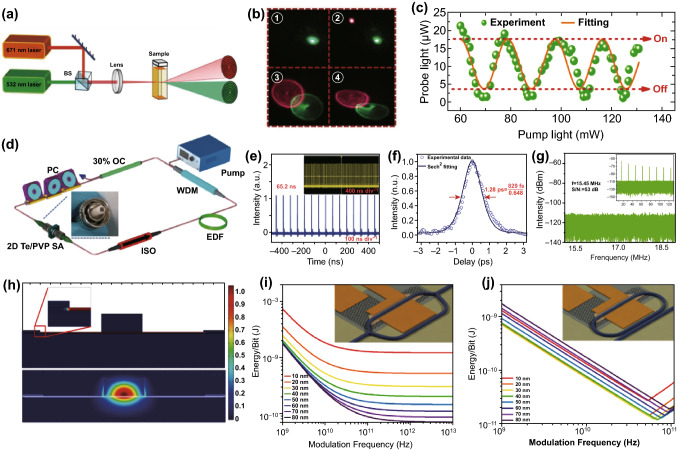
Fig. 15.
a Schematic of the all-optical modulator system based on 2D Te nanoflakes. b Diffraction rings produced by the all-optical modulator system. c Output of the all-optical switcher based on 2D Te nanoflakes as a function of pump laser power including the theoretical fit. Adapted with permission from [184]. Copyright 2019, WILEY–VCH. d Schematic of the mode-locking erbium-doped fiber laser based on a 2D Te/PVP thin film. e Pulse trains from the fiber laser. Inset: 4 μs pulse trains. f Pulse duration of the modulated femtosecond laser. g Radio-frequency spectrum of the fiber laser. Inset: broadband radio-frequency spectrum. Adapted with permission from [185]. Copyright 2019, The Royal Society of Chemistry. h Calculated electric and optical field profiles in the modulator. i Simulated energy consumption of the modulator as a function of frequency for different thicknesses of 2D Te nanoflakes. Inset: schematic of the Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) modulator. j Calculated energy consumption of the Te racetrack modulator as a function of frequency for different thicknesses of tellurene. Inset: schematic of the racetrack modulator. Adapted with permission from [137]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society