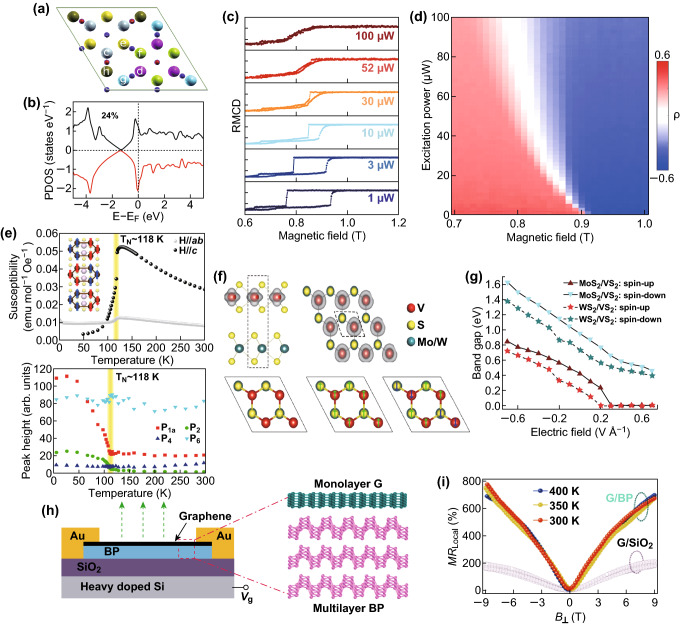
Fig. 7.
Magnetic properties of 2D heterostructures. The broken lattice with six sublattices of graphene on the EuO (a) and the calculated spin polarization in graphene layer (b). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [74]. The RMCD (c) and polarization ρ (d) of WSe2/CrI3 heterostructure under sweeping external magnetic field and different excitation power. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [75]. e The transition of several PL peaks and the magnetic susceptibility along the out-of-plane direction (black) in FePS3 as the temperature increases. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [77]. The spin density and possible magnetic ground state (NM, FM, AFM) of XS2/VS2 heterostructures (f) and the dependence of band gap (g) and electrical field, and the calculated magnetic moment and relative energy is listed in the picture. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [78]. Schematic diagram of the device based on graphene/multilayer BP heterostructure (h) and the huge MR (i) compared with graphene on SiO2 substrate. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [79]