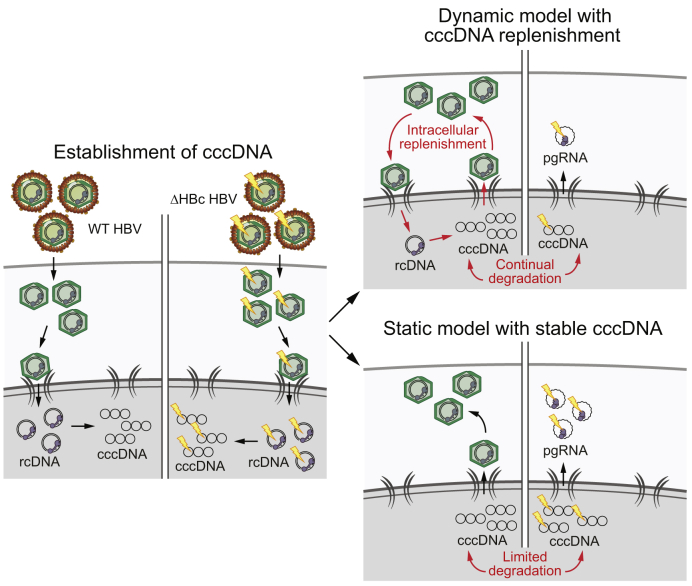
Fig. 1.
Two potential models of cccDNA maintenance in chronic HBV infection.
After initial cccDNA formation (left), the subsequent net stable levels of cccDNA can be maintained by 2 hypothetical models. In the dynamic model of cccDNA maintenance (right), continual degradation and renewal via de novo virions maintain the observed constant levels of cccDNA in an infected cell. However, the static model does not require constant renewal and instead predicts very stable cccDNA molecules. If the dynamic model is valid, we would expect to see a difference in cccDNA levels between WT and ΔHBc HBV infections (decreased in the latter). By contrast, no difference in cccDNA levels would be expected in the static model. cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; HBV, hepatitis B virus; WT, wild-type.