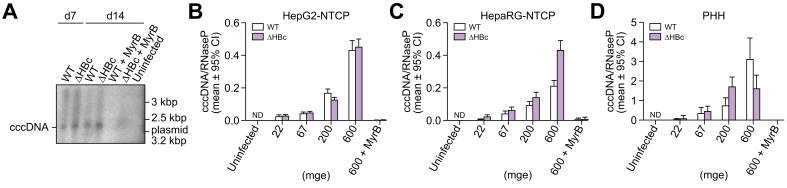
Fig. 3.
HBc expression is not required for the establishment of HBV cccDNA.
(A) HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with WT or ΔHBc HBV at mge 100. At 7 and 14 dpi, cccDNA was extracted and HBV DNA specific Southern blotting was performed. MyrB treatment was used to inhibit infection as control. (B) HepG2-NTCP cells, (C) differentiated HepaRG-NTCP cells, and (D) PHH were infected with WT or ΔHBc HBV with increasing inoculating doses. Total cellular DNA extracted at 7 dpi was analysed by cinqPCR to detect cccDNA levels relative to the single-copy cellular gene RNaseP. The error bars (Poisson 95% CI) represent the technical error of the ddPCR assay. No significant differences in cccDNA levels were detected between WT and ΔHBc HBV-infected cells in any cell line at any inoculating dose. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments. cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; dpi, days post inoculation; HBV, hepatitis B virus; mge, multiplicity of genomic equivalents; ND, not detected; NTCP, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; PHH, primary human hepatocytes; WT, wild-type.