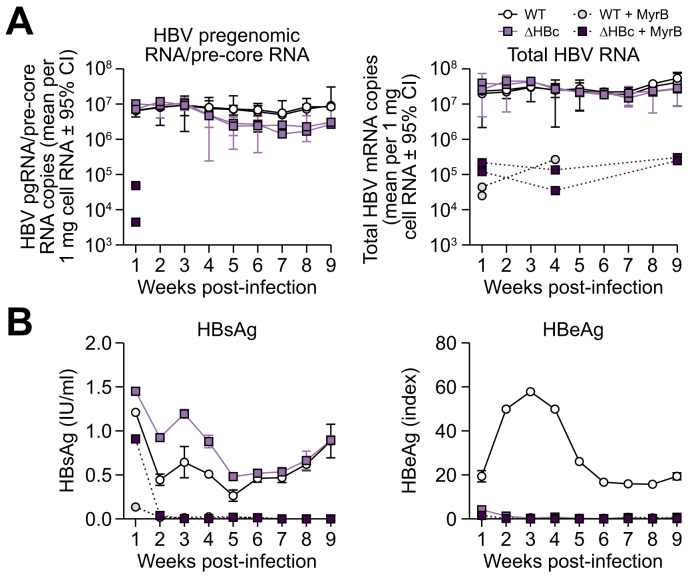
Fig. 5.
De novo HBc expression does not alter viral RNA transcription levels.
(A) HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with WT or ΔHBc HBV at 40 mge. Total cellular RNA was extracted from cells harvested each week and RT-qPCR was performed to detect HBV pgRNA/pre-core mRNA using primers targeting the pre-core region of the HBV genome (left) and total HBV RNA levels using primers targeting HBx reading frame (right). MyrB treatment (dashed lines) was used as control for infection inhibition (1, 4, and 9 weeks post inoculation). Two biological replicates were carried out (separate lines). Error bars (95% confidence interval) represent the technical error of the qPCR performed in triplicate. (B) Supernatant was collected every week and secreted HBsAg (left) and HBeAg (right) levels were measured. The mean of 2 biological replicates (±SD) is shown. Antigen results are representative of 2 independent experiments. HBV, hepatitis B virus; mge, multiplicity of genomic equivalents; NTCP, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; WT, wild-type.