Figure 1.
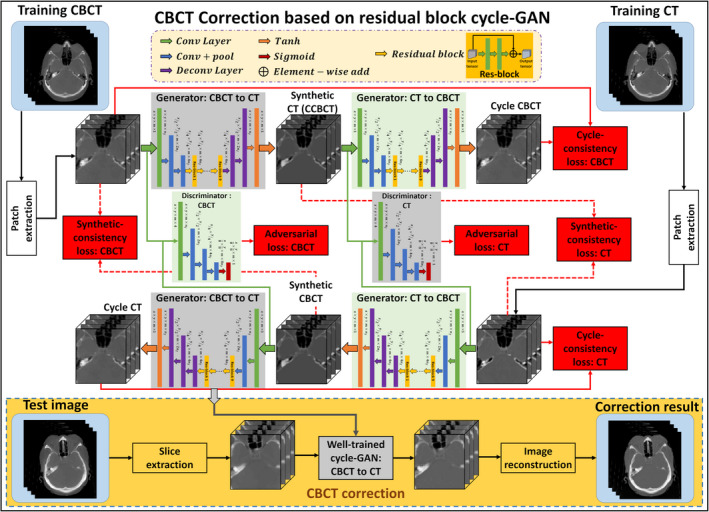
Schematic flow chart of the proposed method. The top region of the figure represents the training stage, and the yellow‐outlined region represents the test stage. During training, patches are extracted from paired cone‐beam computed tomography (CBCT) and CT images. A convolutional neural network is used to downsample the CBCT, and the residual difference between the CBCT and the CT is minimized at this coarsest layer. The synthetic CT (corrected CBCT) image is then upsampled to its original resolution, and a discriminator is trained to learn the difference between this synthetic CT (corrected CBCT) and the planning CT. The inverse of this process is then carried out to generate the cycle CBCT. Simultaneously to training the network to go from CBCT to cycle CBCT, a complementary network is trained to go from planning CT to cycle CT. After training, a CBCT image can be fed into the network which quickly generates a corrected CBCT image. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
