FIG 2.
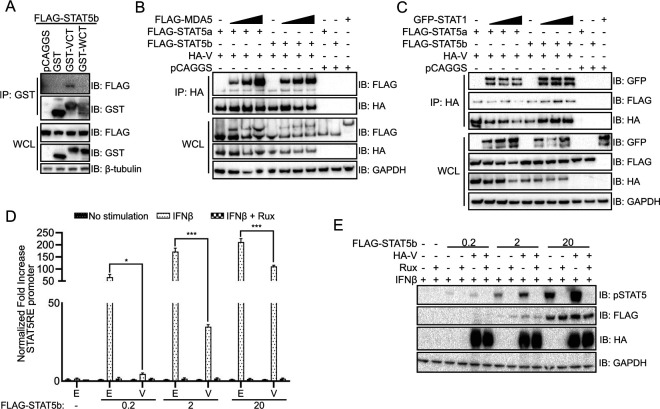
NiV V C-terminus interaction with STAT5 modulates its activity. (A) Co-IP was performed on 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged STAT5b and empty vector control (pCAGGS) or GST alone or fused to the unique C terminus of NiV V or NiV W (GST-VCT and GST-WCT) using glutathione magnetic beads. Western blots were performed for FLAG and GST protein expression in whole-cell lysates (WCL) and bead elutions (IP: GST); the immunoblots (IB) are representative of two independent experiments. (B) A co-IP assay was performed using anti-HA beads on 293T cell lysate transfected with HA-tagged NiV V, FLAG-tagged STAT5a or -5b, and increasing concentrations of MDA5, as indicated. Western blots were performed for anti-HA and anti-FLAG. (C) A co-IP assay was performed as in panel B, on 293T lysates transfected with HA-tagged NiV V, FLAG-tagged STAT5a or -5b, and increasing concentrations of GFP-tagged STAT1. (D) 293T cells were transfected with increasing concentrations of FLAG-tagged STAT5b in 10-fold steps (0 to 20 ng), constitutively expressed Renilla luciferase reporter, STAT5 response element (STAT5RE)-firefly luciferase reporter plasmid, and HA-tagged NiV V, as indicated. Cells were treated with IFN-β and ruxolitinib, as indicated. The firefly luciferase signal was normalized to the Renilla luciferase signal, and the fold increase over mock-treated samples was determined. Error bars represent standard errors of four transfections performed in parallel. The experiment was performed three times. Statistical significance was determined by using a two-tailed t test (*; P < 0.05; ***; P < 0.001). E, empty vector control; V, transfection with HA-NiV V plasmid. (E) Western blot of the panel D luciferase assay samples treated with IFN-β and ruxolitinib, as indicated. Expression of HA-NiV V, Flag-STAT5b, and the phosphorylation status of STAT5b was assessed by Western blotting. IB, immunoblot.