Figure 6.
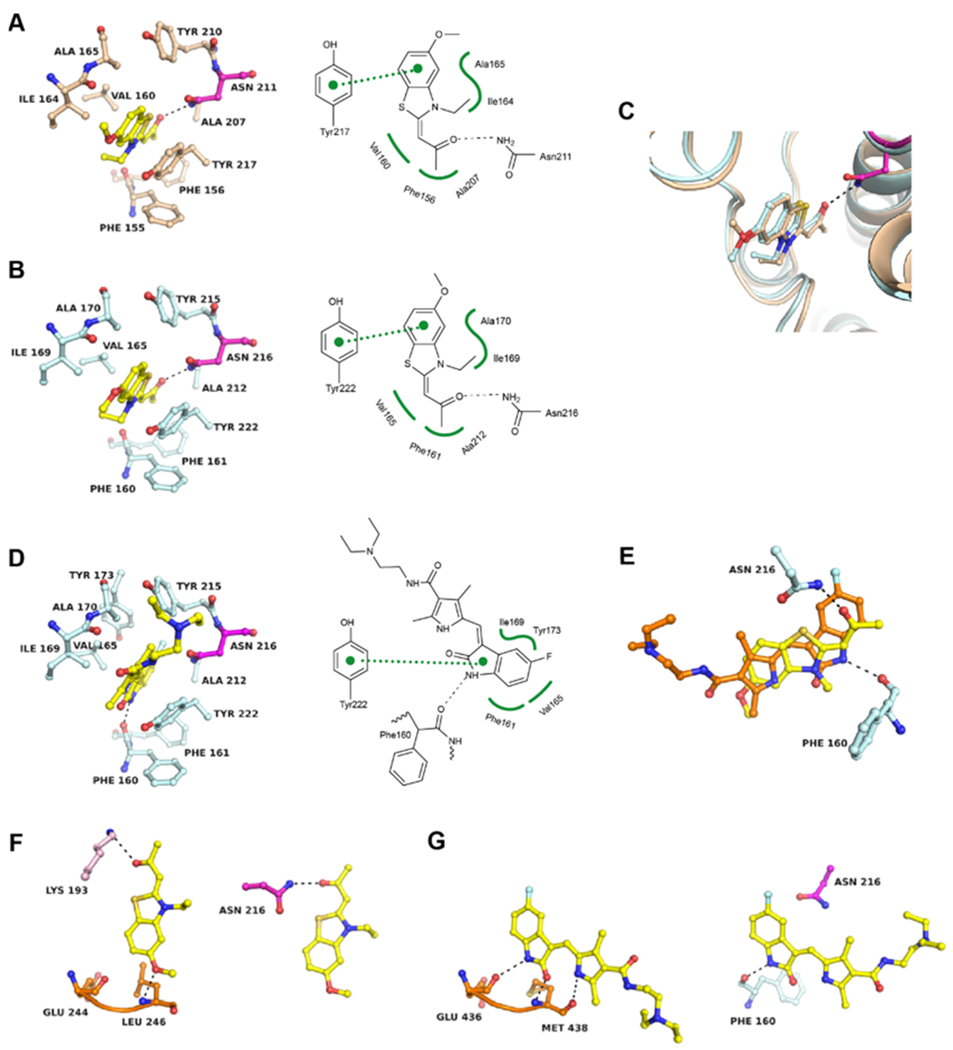
Structural basis of BRD7/9 inhibition by kinase inhibitors. (A) Cocrystal structure of TG003 in BRD7 (PDB 6V0Q) and (B) in BRD9 (PDB 6V0S). (C) Superposition of both structures. (D) Cocrystal structure of BRD9 liganded with sunitinib (PDB 6V0X). (E) Superposition of TG003 (yellow) and sunitinib (orange) bound to the KAc site of BRD9. (F) Comparison of the binding mode of TG003 in the ATP site of CLK2 (PDB 6FYI) (left panel) and the KAc site of BRD9 (right panel). The kinase hinge region is colored in orange and other kinase residues are colored in pink. (G) Comparison of the binding mode of sunitinib in the ATP site of ITK (PDB 3MIY) (left panel) and the KAc site of BRD9 (right panel). 2Fo – Fc and Fo – Fc electron density maps are shown in the Supporting Information Figures S3 and S4.
