Figure 1:
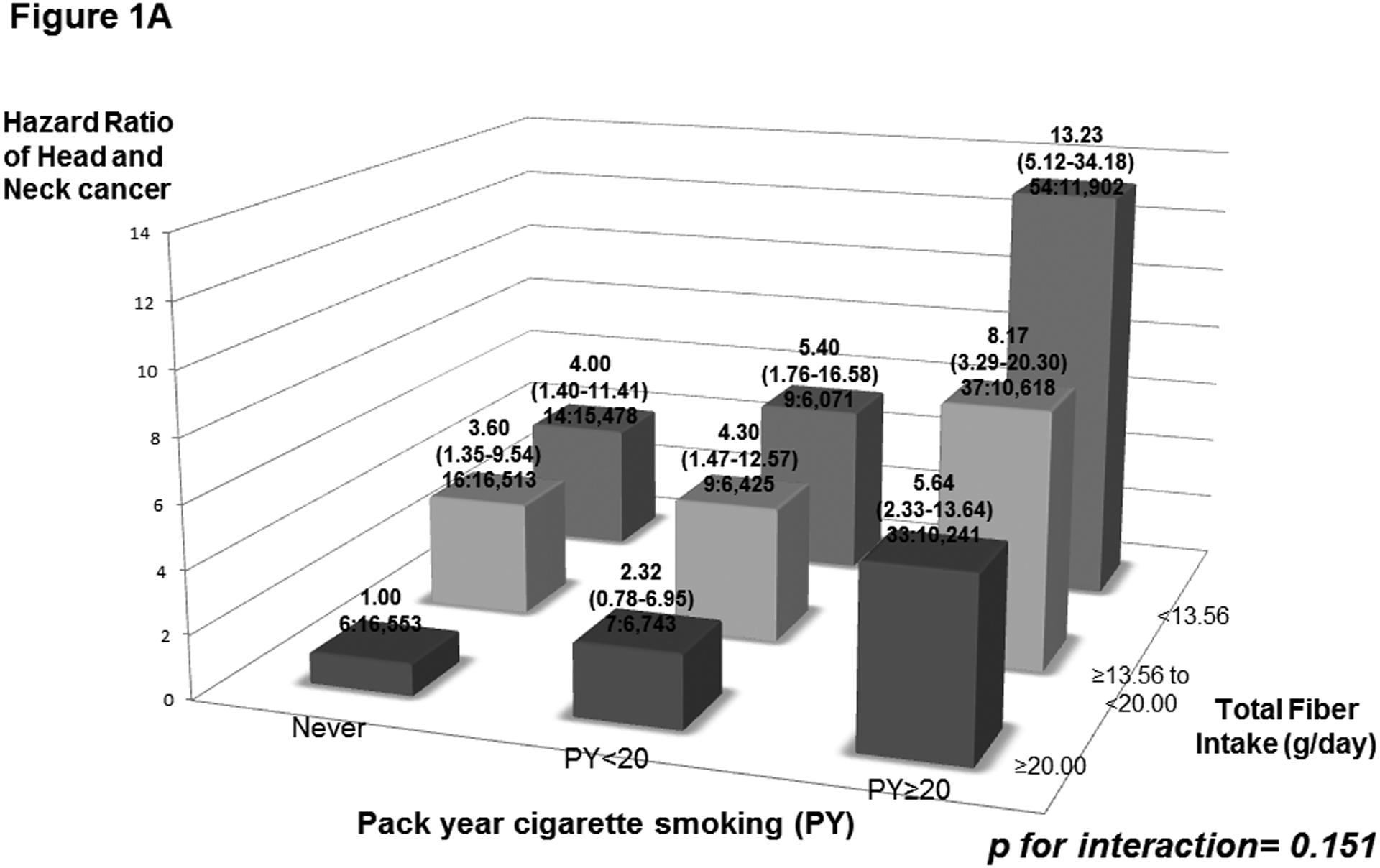
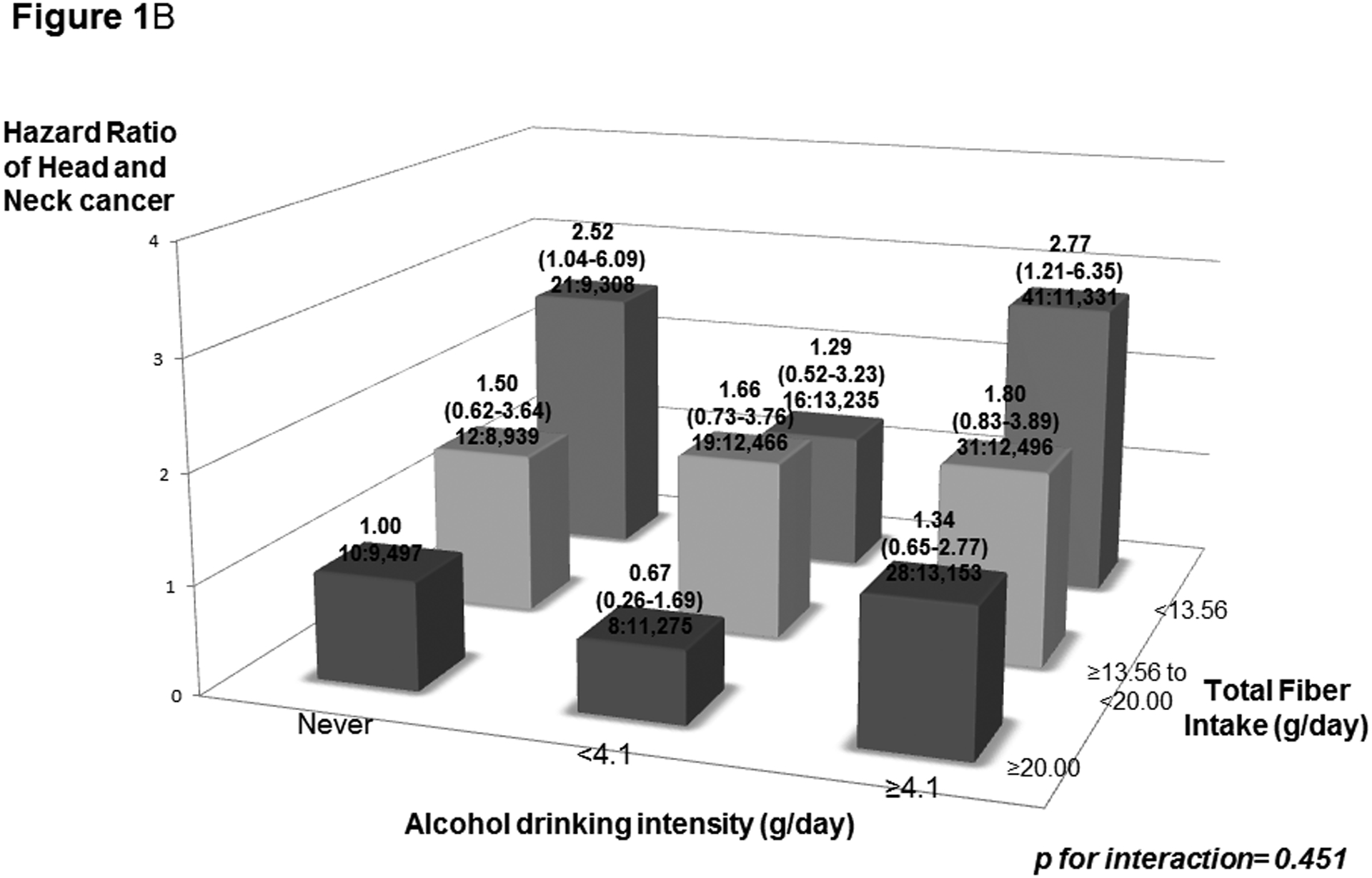
Hazard ratios (HRs) of head and neck cancer, and corresponding confidence intervals (95% CIs), according to pack year cigarette smoking (PY) (Figure 1A) or alcohol drinking intensity (g/day) (Figure 1B) and total fiber intake (g/day). The HRs were derived from Cox proportional hazard models adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, education, race/ethnicity, pipe smoking status, cigar smoking status, cigarette smoking status, pack-year cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking status, alcohol drinking intensity, non-alcohol total energy, total vegetable and fruit intake, and marital status. The number of cases and controls within each category was indicated below the corresponding HR as: “number of cases : number of controls.” We found no significant interaction of smoking and drinking with total fiber intake on HNC risk.
