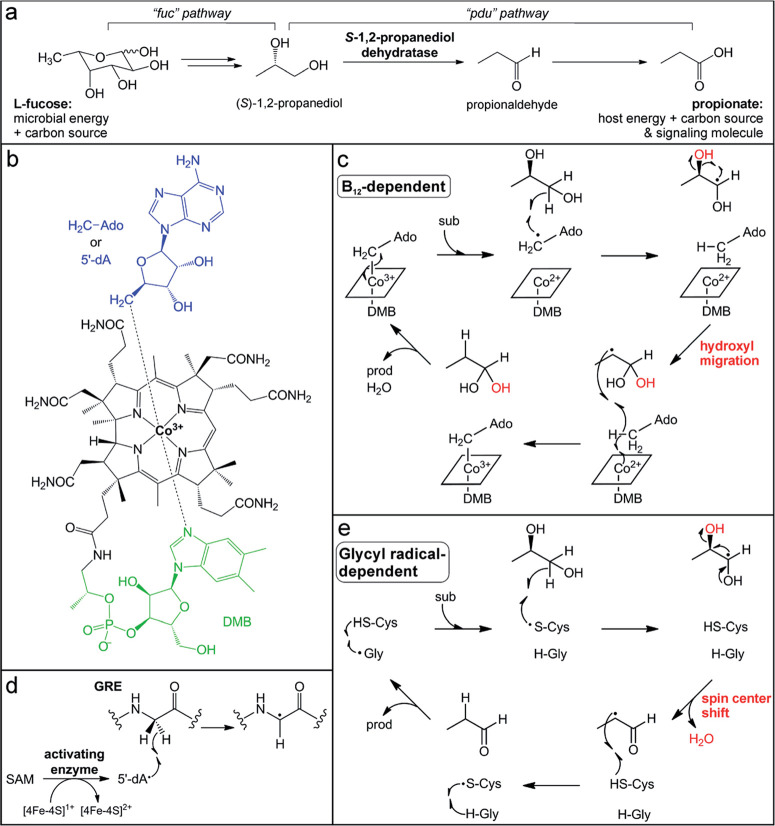
Fig. 2.
Participation of B12-dependent and glycyl radical-dependent enzymes in gut microbial L-fucose metabolism. (a) Propionate generation via the L-fucose and (S)-1,2-propanediol utilization pathways (fuc and pdu, respectively). (b) Structure of adenosylcobalamin in the “base-on” form. (c) Proposed mechanism for (S)-1,2-propanediol dehydration catalyzed by the B12-dependent enzyme PduC invoking a hydroxyl migration step. (d) Glycyl radical installation by the radical SAM activating enzyme. (e) Proposed mechanism for (S)-1,2-propanediol dehydration catalyzed by the GRE dehydratase involving a spin center shift.