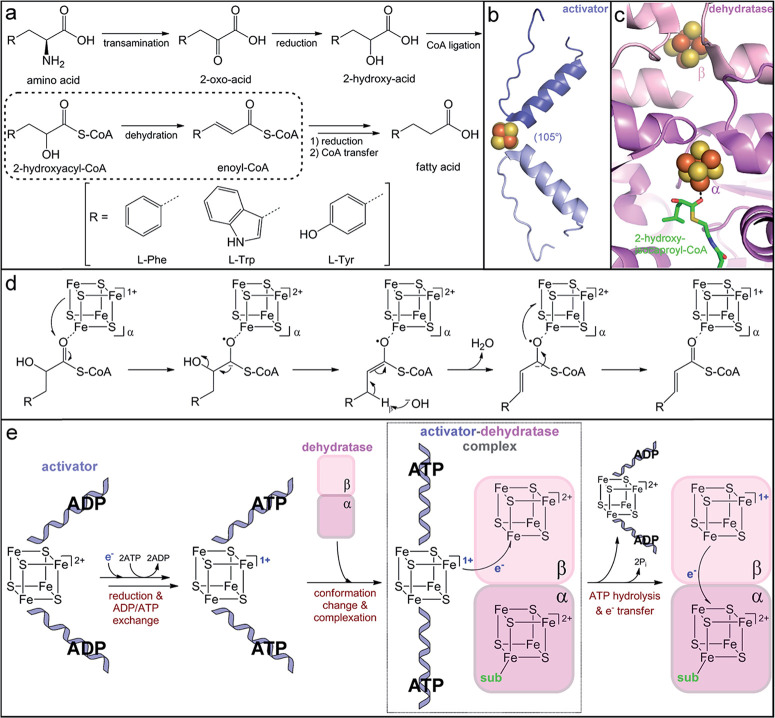
Fig. 6.
Production of immune-modulatory indole derivatives by gut-associated Clostridia. (a) Reductive amino acid fermentation pathway involving dehydration of a 2-hydroxy-acid. (b) Homodimer interface of the dehydratase activator (2-hydroxyisocaproyl-CoA dehydratase activator, PDB accession code: 4EHT) highlighting the helix–cluster–helix motif in the ADP-bound 105o angle conformation. (c) Heterodimer interface of the dehydratase component (2-hydroxyisocaproyl-CoA dehydratase, PDB accession code: 3O3N) depicting the [4Fe–4S] clusters in each subunit and the direct substrate coordination to the a-cluster. (d) Umpolung charge reversal mechanism of 2-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydration. (e) Proposed ATP-dependent electron transfer mechanism of dehydratase activation.