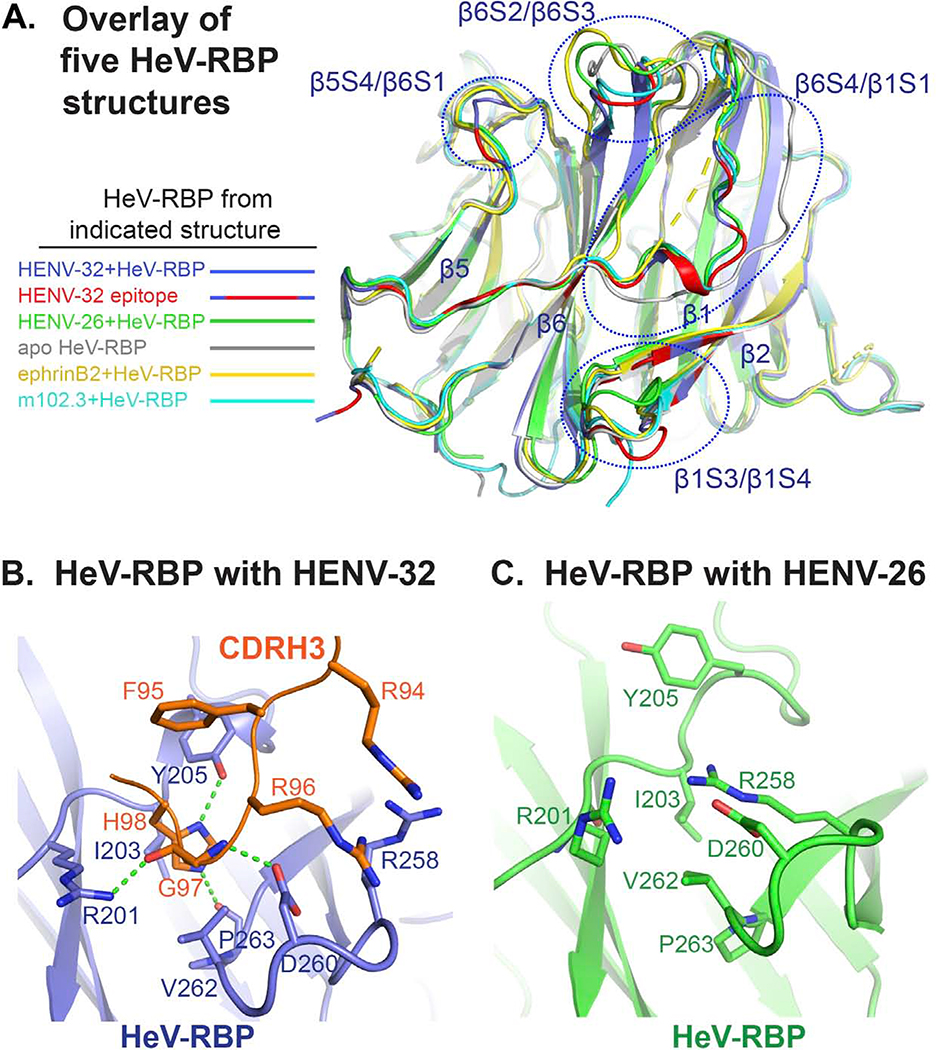
Figure 5. Functional significance of conformational changes of HeV-RBP head domain upon HENV-32 binding.
A) Overlay of five HeV-RBP head domain crystal structures. All structures are shown as cartoon representation. Light blue: HeV-RBP in the HENV-32/HeV-RBP complex, and the epitope recognized by HENV-32 is highlighted in red; white: HeV-RBP apo form; yellow: HeV-RBP in the ephrinB2/HeV-RBP complex; green: HeV-RBP in the ENV-26/HeV-RBP complex; cyan: HeV-RBP in the mAb m102.3/HeV-RBP complex.
B) Structural details of the binding interface of HENV-32 CDRH3 and HeV-RBP head domain. Interacting residues are shown as stick representation, and the hydrogen bonds between CDRH3 and HeV-RBP are shown as broken green lines.
C) Structural details of HENV-32 CDRH3 binding site in the crystal structure of the HeV-RBP/HENV-26 complex are shown for comparison. Residues interacting with the HENV-32 CDRH3 are shown as sticks. Comparison of the two structures of HeV-RBP head domain reveals extensive conformational changes at the site caused by CDRH3 binding. In the crystal structure of HENV-32/HeV-RBP complex, HENV-32 CDRH3 residue H98 is surrounded by a pocket on HeV-RBP formed by residues I203, Y205, V262, and P263, while in the crystal structure of HENV-26/HeV-RBP complex, there is no pocket at this site. The strong ionic bonding between HeV-RBP residues R258 and D260 forms a lid covering the site. HENV-32 HCDR3 remodels the site by inducing an outward flipping of the main chain of the β1/S3-S4 loop, residues L256 – S264, and corresponding side chain rearrangements (especially the outward flipping of R258 side chain). The major driving force for this induced fit might be the interactions between HENV-32 R94/R96 and HeV-RBP R258/D260, and interaction of HENV-32 H98 with the surrounding cavity residues of HeV-RBP.