Figure 1. Part of a lampbrush chromosome bivalent from Xenopus laevis.
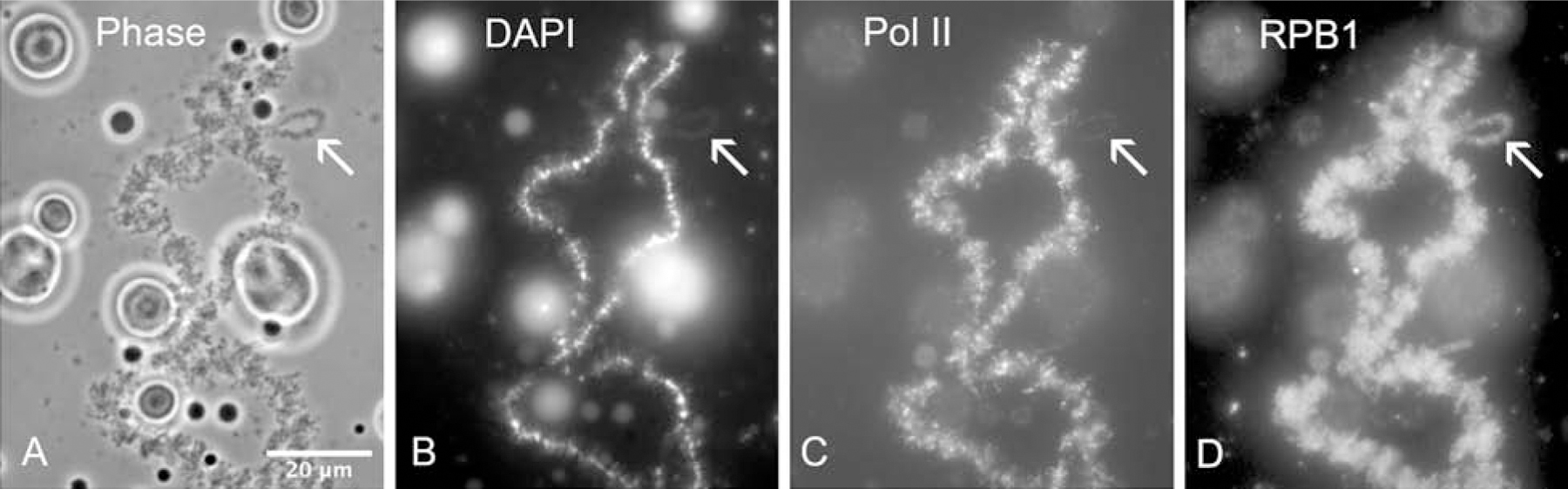
(A) Part of one bivalent from a control GV, showing loops extending laterally from the chromosome axes. An arrow indicates an especially large loop. The loops represent regions of active transcription. Several large extrachromosomal nucleoli are visible in this field. Phase contrast. (B) The same field stained with the DNA-specific dye DAPI. DNA is evident in the chromomere axis of the chromosome, as well as in the core of the nucleoli. (C) Staining with antibody H14 (against phosphorylated pol II) demonstrates active transcription on the lateral loops of the chromosomes. (D) An antibody against RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 (clone 8WG16) stains the lateral loops.
