Figure 1. Epigenetic Regulation of Stemness in Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) Clusters and Single CTCs.
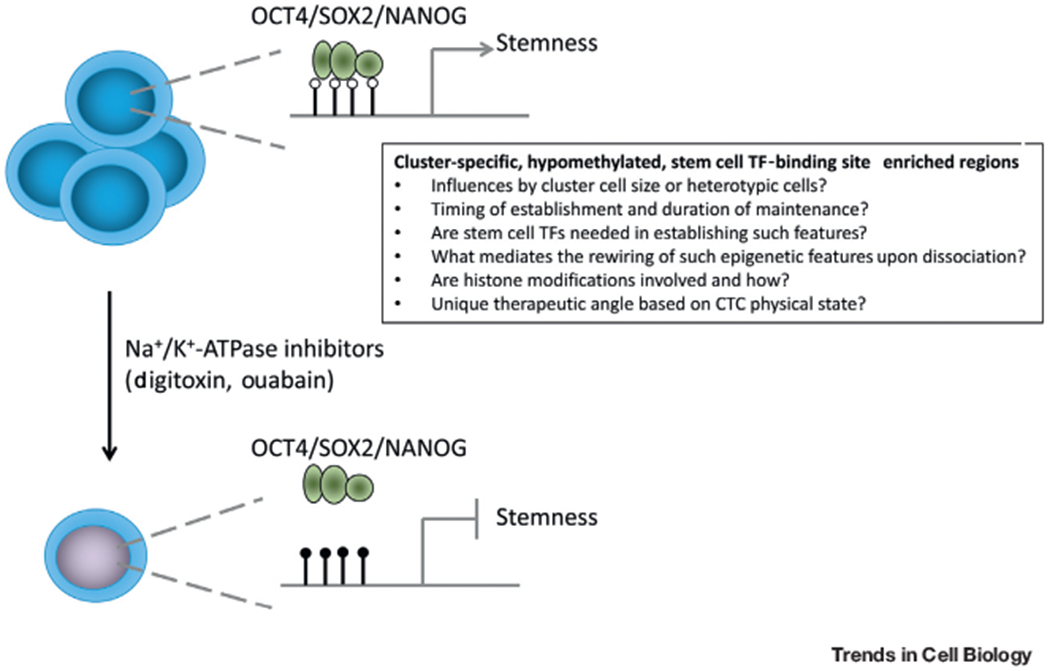
By comparing DNA methylation differences between CTC clusters and single CTCs, the authors discovered that hypomethylation regions in CTC clusters are enriched with embryonic stem cell transcription factor (TF) binding sites (e.g., OCT4, SOX2, NANOG), which correlated with stemness-related transcriptional pathways and metastatic phenotype. Upon dissociation of CTC clusters into single CTCs via treatment with Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitors, the cluster-specific hypomethylated regions gained methylation and reduced the accessibility of TFs, leading to suppression of stemness phenotype. This exciting finding has raised new questions related to dynamic epigenetic regulation and some of the examples are listed in the box.
