Figure 1.
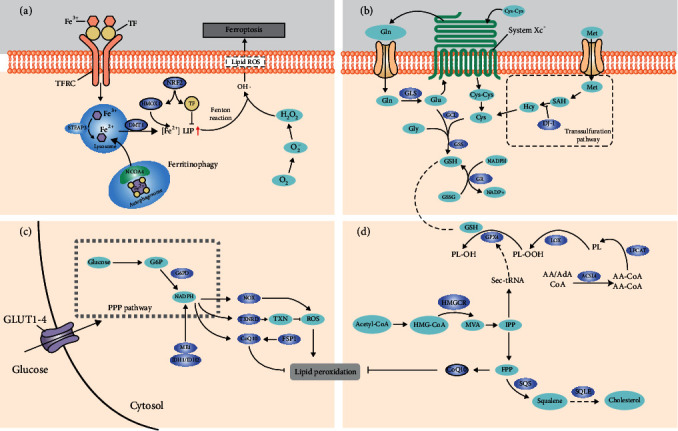
The central metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. (a) Transferrin, TFRC, and NCOA4 regulate iron sequestration by increasing the levels of [Fe2+] LIP, thus triggering lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. (b) System Xc− (composed by SLC7A11 and SLC3A2) exchanges intracellular glutamate for extracellular cystine, thereby supporting intracellular glutathione (GSH) synthesis, which is the primary endogenous antioxidant. GPX4 uses GSH to detoxify lipid hydroperoxide, thus protecting tumor cells against ferroptosis. And the transsulfuration pathway affects ferroptosis sensitivity by providing cysteine for GSH synthesis. (c) NADPH can be used for the regeneration of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) by glutathione reductase (GR). There are three significant ways for intracellular NADPH production—produced from pentose phosphate pathway, produced by isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and IDH2 through the conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate, and malic enzyme 1 (ME1) through the transformation of malate to pyruvate. In addition to GSH regeneration, the regeneration of thioredoxin (TXN) and the activity of CoQ10 are also required for the participation of NADPH to eliminate ROS and antiferroptosis. And in some cellular contexts, NADPH can be oxidized by NADPH oxidase (NOX), thus increasing intracellular ROS levels. (d) Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) produced from the mevalonate pathway is required for the cholesterol biosynthesis, Sec-tRNA, and CoQ10 production, which all can be used to regulate ferroptosis sensitivity. Sec-tRNA is essential for the integration of GPX4 with selenocysteine. TF: transferrin; DMT1: divalent metal transporter 1; TFRC: transferrin receptor; STEAP1: STEAP family member 1; NCOA4: nuclear receptor coactivator 4; LIP: labile iron pool; GLS: glutaminase; GCL: glutamate-cysteine ligase; GSS: glutathione synthetase; GR: glutathione reductase; DJ-1: also known as Parkinsonism-associated deglycase: PARK7; G6PD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; ME1: malic enzyme 1; IDH1/IDH2: isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2; NOX: NADPH oxidase; TXNRD: thioredoxin reductase 1; CoQ10: coenzyme Q10; TXN: thioredoxin; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; MVA: mevalonate; IPP: isopentenyl pyrophosphate; FPP: farnesyl pyrophosphate; SQS: squalene synthase; SQLE: squalene monooxygenase; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; LOX: lipoxygenase; ACSL4: acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3: lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3.
