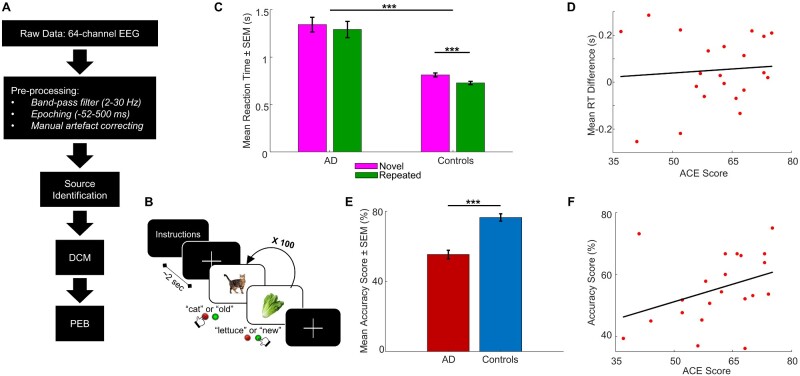
Figure 1.
Analysis pipeline, task structure and task performance across patients and controls. (A) Schematic of the EEG data analysis pipeline, from collection and pre-processing of raw EEG data, through source identification, to constructing our DCMs and analysing our DCMs using PEB. (B) Visual mnemonic priming and recognition task structure. Subjects were presented with an image of an object and were instructed to covertly name the object (priming task) or indicate whether the object was old or new (recognition task), for 100 trials per task. (C) Mean RTs ± SEM for novel and repeated trials in the priming task, in patients and controls. Controls had significantly faster RTs across trial types than patients, and controls had significantly faster RTs in repeated trials compared to novel trials. (D) No correlation between ACE scores and mean RT differences for patients only in the priming task. (E) Mean accuracy scores ± SEM in the recognition task, in patients and controls. Controls had significantly higher accuracy scores compared to patients. (F) Strong correlation between ACE scores and accuracy score for patients only in the recognition task. AD = Alzheimer’s disease; SEM = standard error of mean. ***P < 0.001.