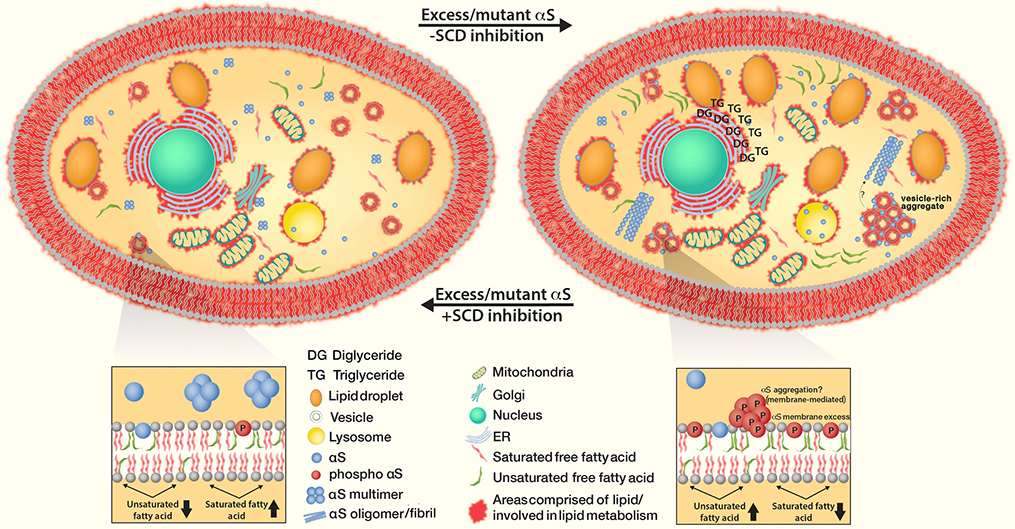
Fig. 6 :
SCD inhibition restores αS-Induced diglyceride (DG) accumulation in the ER, trafficking defects as well as increased triglycerides (TG) and lipid droplets. The treatment reduces clusters of vesicles when excess αS monomers accumulate and form cytoplasmic inclusions (as well as αS fibrillization that might be downstream). Decreased SCD activity prevents membrane defects, decreases αS phosphorylation and restores intact equilibria between αS monomers vs. physiological helical tetramers as well as cytosolic vs. membrane-associated αS.