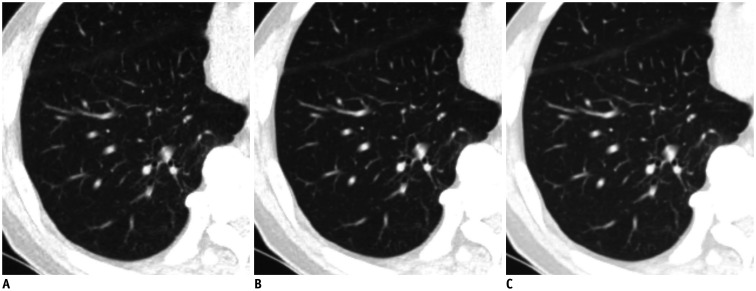
Fig. 1. Comparison of low-dose chest CT scan in axial lung window images of lung in 73-year-old man.
Reconstruction was performed with ASiR-V 30% (A), DLIR-M, (B) and DLIR-H (C). Signal did not significantly vary across different reconstructions. However, image noise of DLIR images was lower than that of ASiR-V 30% images (ASiR-V 30% vs. DLIR-M, p = 0.018 and ASiR-V 30% vs. DLIR-H, p < 0.001, respectively). Image noise in lung did not significantly differ between DLIR-M and DLIR-H (p = 0.837). ASiR-V = adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction-Veo, CT = computed tomography, DLIR = deep-learning image reconstruction, DLIR-H = DLIR at high levels, DLIR-M = DLIR at medium levels