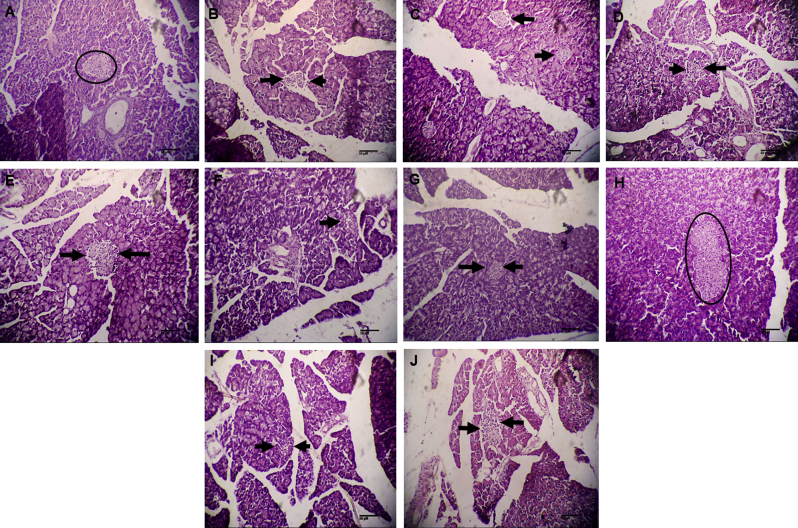
Fig. 3.
(A) Pancreatic tissue section is unremarkable and shows normal islets of Langerhans in normal control group (H&E; 100X) (B) Photomicrograph shows degenerated islets of Langerhans replaced by fibrosis in diabetic control group (H&E; 100X) (C) Photomicrograph shows normal islets of Langerhans and features like binucleation and eosinophilia in positive control (H&E; 100X) (D) Section showing fibrotic islets of Langerhans in MeOH extract (200 mg/kg) treated group (E) Section showing mildly preserved islets of Langerhans in MeOH extract (400 mg/kg) treated group (H&E; 100X) (F and G) Photomicrographs showing degeneration of islets of Langerhans and lymphocytic infiltration in ethyl acetate fraction (100 and 200 mg/kg) treated groups (H&E; 100X) (H) Section showing preserved integrity of islets of Langerhans and hyperplasia of islet cells, exhibiting protective response to large dose of ethyl acetate fraction (400 mg/kg) (H&E; 100X) (I and J) Photomicrographs showing degenerated islets of Langerhans in mother liquor (200 and 400 mg/kg) treated groups (H&E; 100X).