Figure 5.
Comprehensive epigenome contributes to hPSC maintenance
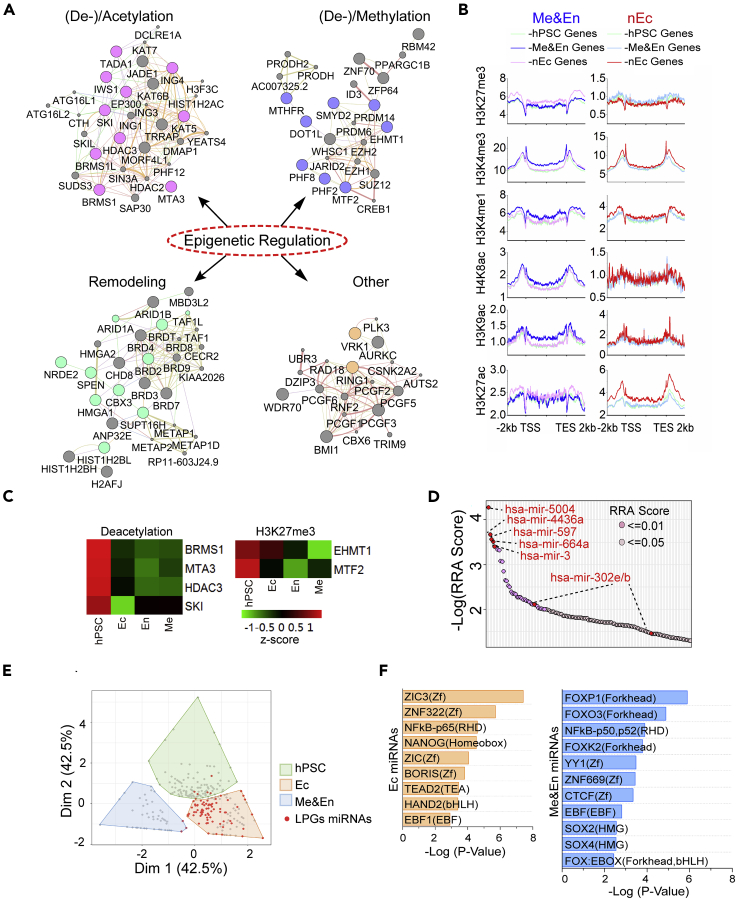
(A) Four epigenetic regulation clusters as labeled were highlighted in LPGs. Networks were constructed by using GeneMANIA integrated with Cytoscape visualization. Within each tightly inter-connected cluster, colored nodes represented the genes identified in LPGs.
(B) Profiling histone modifications (HMs) of hESC-, mesendoderm (Me&En)-, and nEc-specific genes in hPSCs differentiated Me&En or nEc lineages. Histone acetylation, H3K4me1, and H3K4me3 of lineage-specific genes were significantly increased, and H3K27me3 were decreased during corresponding lineage specification.
(C) Heatmap showing a decreased expression of core regulators for histone deacetylation and H3K27me3 along with trilineage specification of hPSCs. The expression level was normalized to RPKM and z-scored.
(D) miRNAs within the scope of LPGs were identified by MAGeCK algorithm. The significance of each miRNA was ranked through RRA. Each dot of the scatterplot represented one single miRNA and top 5 miRNA, as well as hsa-mir-302e/b known for regulating self-renewal of hPSCs were labeled in red.
(E) Among all miRNAs in miRBae, hPSCs-, Ec-, or Me&En-related miRNAs were defined by using PCA classifier according to the enrichment score of all 3 categories based on GO annotation of its target genes. Red dots represented miRNAs shown in defined LPGs, and they were highly enriched in the Ec-related group.
(F) Motif analyses with HOMER for the promoter regions of Ec- or Me&En-related miRNAs.