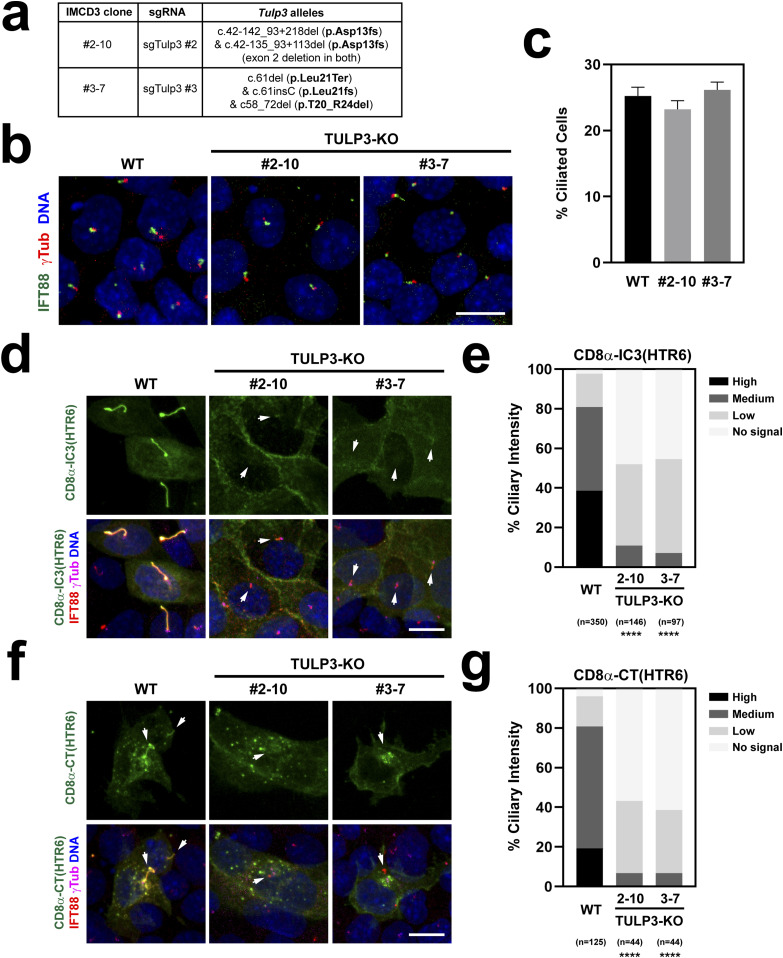
Figure 11. TULP3 regulates both CTS1 and CTS2 function.
(A) Genomic characterization of the two CRISPR-generated TULP3-KO IMCD3 clones used in this figure. Allele nomenclature corresponds to Ensembl mouse transcript Tulp3-201 and follows Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS) guidelines (52). (B) TULP3-KO clones still form cilia, as seen by immunostaining with IFT88 (green) and g-tubulin (red) antibodies. DAPI in blue. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B, C) Percentage of ciliated cells was quantitated from (B). Data are mean ± SEM of n = 33 fields of cells, each containing at least 30 cells, from two coverslips. No significant differences were found by one-way ANOVA. (D) CD8α-IC3(HTR6)-Stag-TEV-EYFP was transfected into TULP3-KO clones, or WT IMCD3 cells as control, and its ciliary localization assessed by immunostaining with Stag (green), IFT88 (red), and g-Tubulin (magenta) antibodies. DAPI-stained nuclei in blue. CD8α-IC3(HTR6) levels are very low or undetectable in TULP3-KO cilia (arrows). Scale bar, 10 μm. (D, E) Quantitation of CD8α-IC3(HTR6) ciliary intensity from (D). The percentage of cilia in each of the indicated categories is shown. The number of transfected cell cilia counted in each condition is displayed at the bottom, together with statistical significance from chi-square tests comparing each mutant distribution to that of WT (P < 0.0001 (****)). (D, F) Same analysis as in (D) was performed for CD8α-CT(HTR6)-Stag-TEV-EYFP, which again localizes to WT but very weakly or not at all in TULP3-KO cilia (arrows). (E, F, G) Quantitation of CD8α-CT(HTR6) ciliary intensity from (F) was performed and analyzed as in (E).