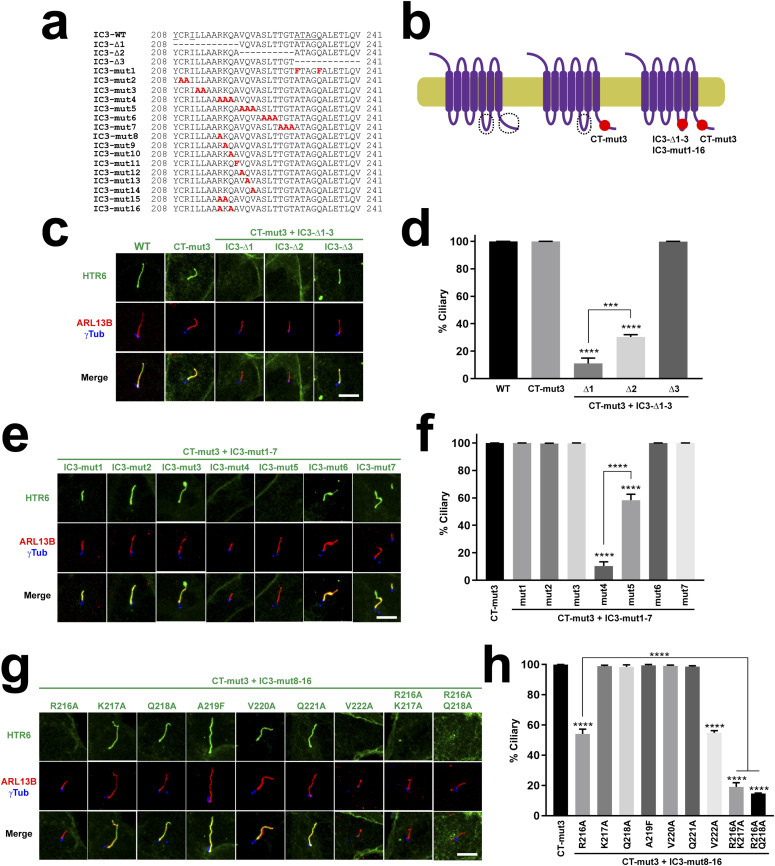
Figure 5. An RKQ motif is critical for IC3-dependent HTR6 ciliary targeting.
(A) Sequence of HTR6’s IC3 loop and its mutants used here. (B) Schematic of HTR6 wild type and its mutants used here. CT-mut3 is the mut3 CTS2 mutation from Fig 3. The IC3 mutations from (A) were combined with CT-mut3. Mutations shown as red spots. CTS1 and CTS2 encircled with dashed lines when intact. (C) IMCD3 cells expressing the indicated versions of HTR6, all fused to C-terminal EGFP, were analyzed by immunofluorescence with antibodies against EGFP (green), ARL13B (red) and gamma-tubulin (γTub, blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. (C, D) Percentage of G protein-coupled receptor-positive cilia relative to total transfected-cell cilia was quantitated for the constructs in (C). (C, E) The indicated HTR6 mutants were analyzed as in (C). (D, E, F) Ciliary targeting of HTR6 mutants from (E) was quantitated as in (D). (C, G) The indicated HTR6 mutants were analyzed as in (C). (D, G, H) Ciliary targeting of HTR6 mutants from (G) was quantitated as in (D). Data in (D, F, H) are mean ± SEM of n = 3–4 independent experiments per construct, with at least 50 cilia counted per construct and experiment. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests. Unless otherwise indicated, significance is shown relative to control sample (black column) with P < 0.001(***) or P < 0.0001(****).