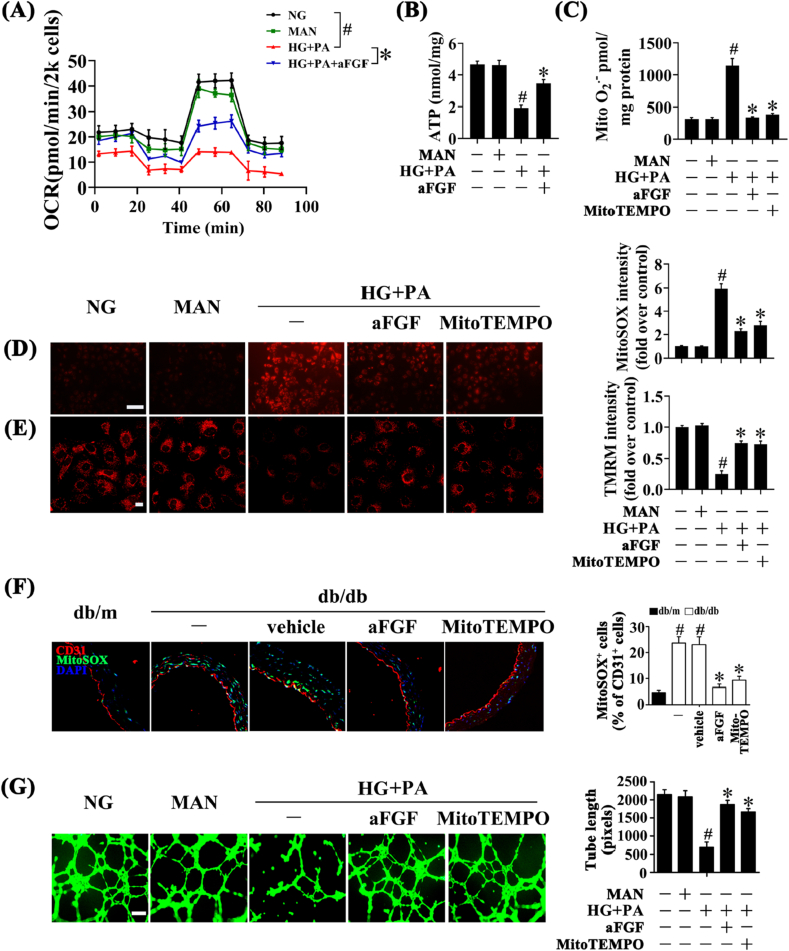
Fig. 2.
aFGF lowered the level of mitochondrial superoxide in vascular endothelial cells. (A) OCR was analysed using a Seahorse XF analyser. (B) ATP production in HUVEC. (C) Mitochondrial O2•− in HUVEC was measured by mitochondria targeted probe MitoSOX and UPLC after accumulation of O2•−-specific product 2-OH-Mito-E+. (D) mtROS of HUVECs was detected by MitoSOX staining assay, scale bars = 1000 μm. HUVECs were cultured either in NG or HG + PA medium in the presence or absence of aFGF (100 ng/mL) or MitoTEMPO (10 μM) for 72 h. MAN was served as the osmotic control for the HG + PA. (E) Mitochondrial membrane potential of HUVECs was detected by TMRM fluorescence staining, scale bars = 5 μm. (F) Representative confocal images of MitoSOX stained aorta tissue sections, scale bars = 20 μm, from db/m mice, db/db mice, and intraperitoneal aFGF (0.5 mg/kg) or MitoTEMPO (0.7 mg/kg) treated db/db mice. (G) Capillary-like tube formation of HUVECs, scale bars = 300 μm. All values displayed are means ± SEM of 6 independent experiments. For (A)-(E) and (G), #p < 0.05 vs. NG or MAN; *p < 0.05 vs. HG + PA; For (F), #p < 0.05 vs. db/m mice; *p < 0.05 vs. db/db mice or vehicle treated db/db mice.