Fig. 4. Functional characterization of SZ-associated ASoC SNPs.
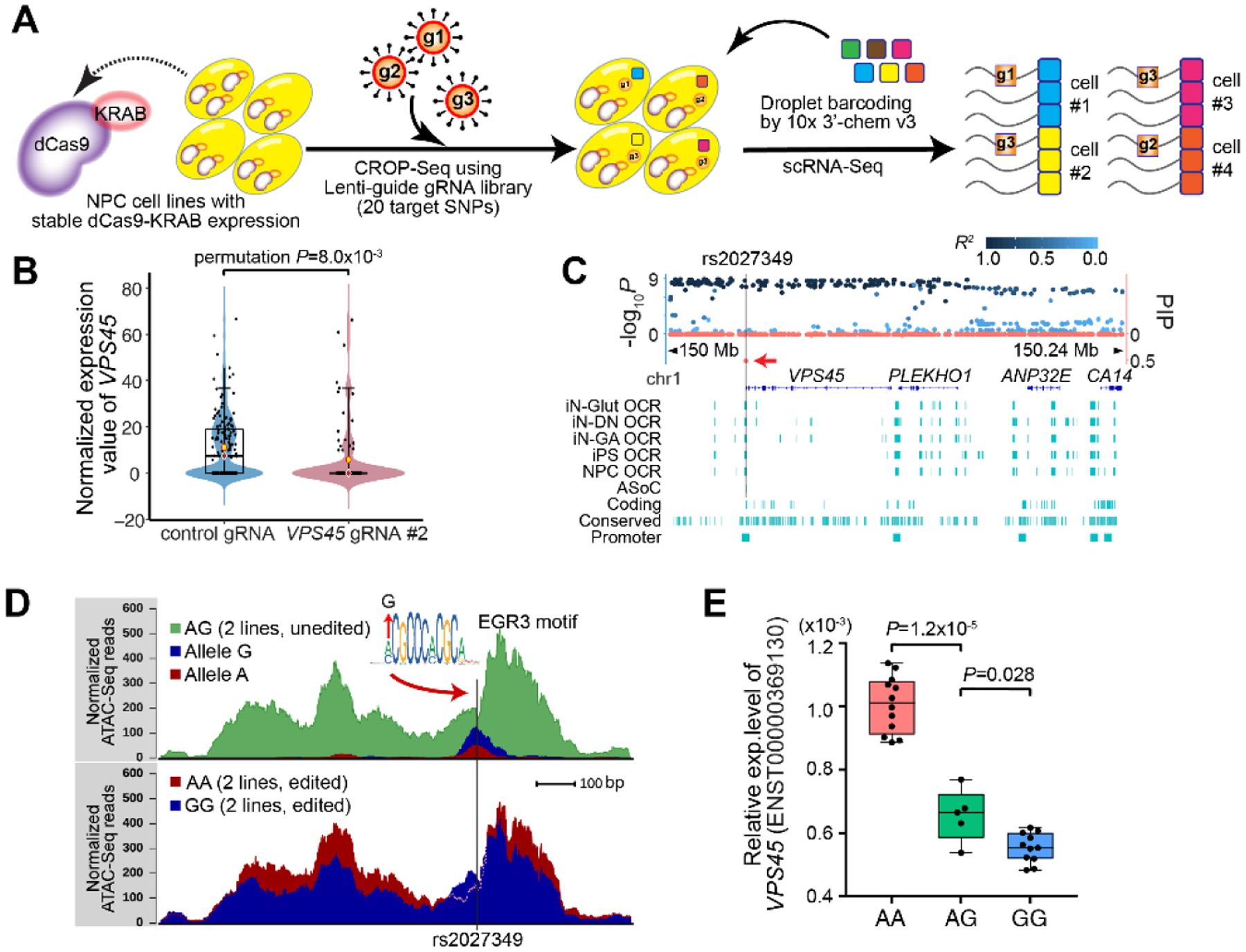
(A) Schematic of the modified CROP-seq (7) to screen cis-targets of the 20 ASoC sites. (B) Reduced VPS45 expression in single NPCs expressing gRNAs targeting rs2027349. (C) Fine-mapping the VPS45 (rs2027349) locus. Left y-axis: −log10 p-values from SZ GWAS (10) (points above the x-axis); right y-axis: PIPs (points below the x-axis, red). Vertical bar: rs2027349. (D) CRISPR-editing rs2027349 altered local OCR accessibility in isogenic NPCs (AA vs GG; 2 lines/genotype). The G allele disrupts the EGR3 motif; note that AA lines showed higher (more accessible) peak but with a lower ATAC-seq signal at the EGR3-binding site likely due to A allele’s stronger EGR3-binding that prevents transposase from accessing. (E) Editing rs2027349 altered VPS45 expression in NPCs (major transcript ENST00000369130; by qPCR). VPS45 expression was normalized to GAPDH. Two iPSC lines (AG at rs2027349) were edited to isogenic lines with AA or GG genotype, each with 2–3 clones (n=2–3 independent cultures). Student’s t-test (Welch’s correction) was used.
