Fig. 1.
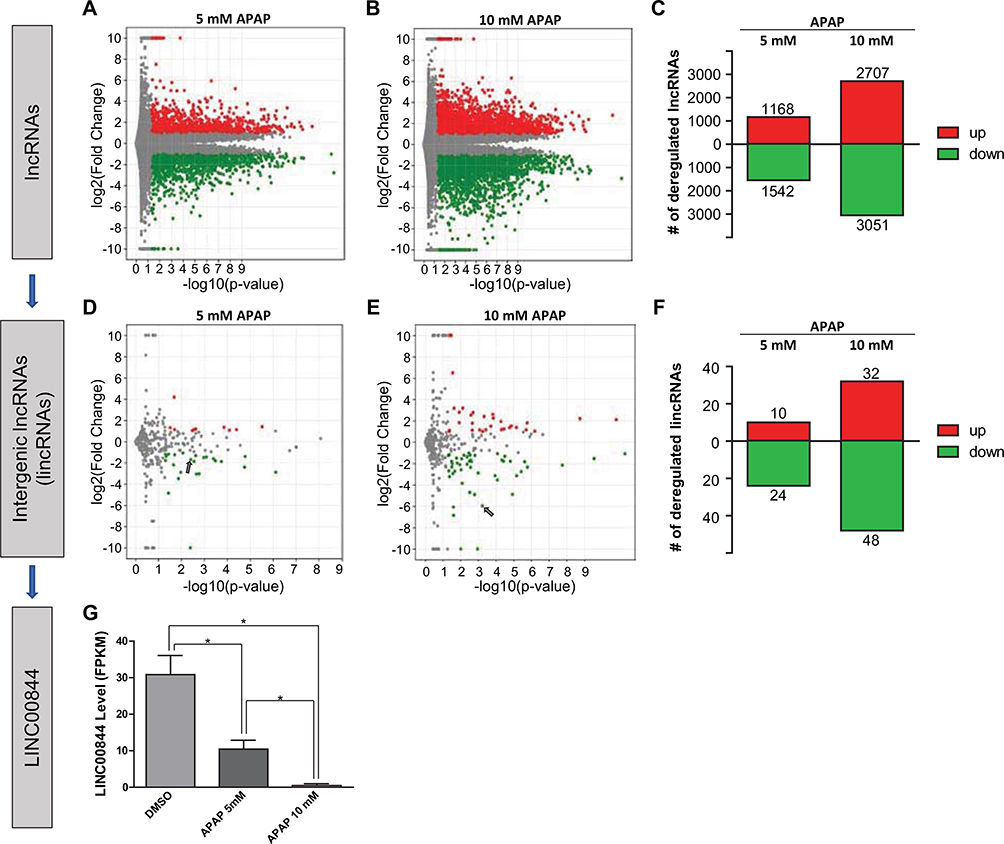
Identification of LINC00844 as a hepatotoxicity-associated lncRNA candidate. In HepaRG cells treated with 5 and 10 mM APAP, 27,660 lncRNAs were identified, among which 1168 and 2707 were significantly upregulated whereas 1542 and 3051 were significantly downregulated (a–c, log2(fold change) > 1 or < − 1 and p < 0.05). Among all lncRNAs, 559 lincRNAs were identified using the term “LINCxxxxx” (“x” represents a single digit). 10 and 32 lincRNAs were significantly upregulated, whereas 24 and 48 were significantly downregulated by 5 and 10 mM APAP treatment (d–f, log2(fold change) > 1 or < − 1 and p < 0.05). Among significantly deregulated lincRNAs, substantially deregulated lincRNAs were selected using more stringent cut-offs, log2(fold change) > 5 or < − 5 and p < 0.001. LINC00844 was the only lincRNA that met these criteria. In HepaRG cells, LINC00844 was significantly downregulated by APAP treatment in a concentration-dependent manner (d, e, arrow; and g). Results shown are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05