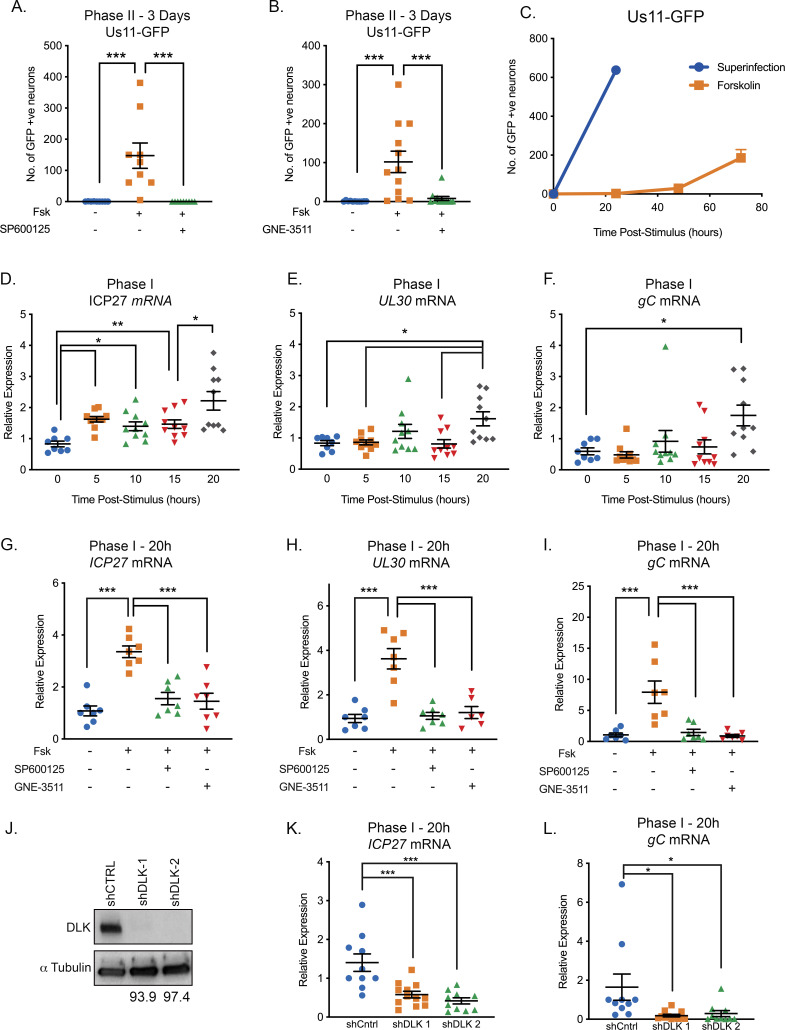
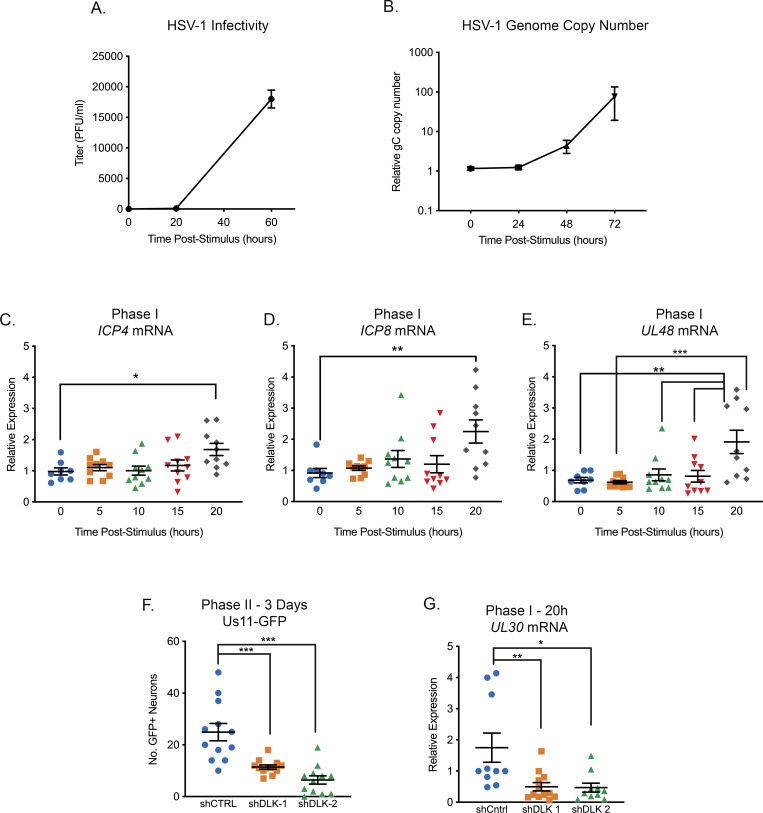
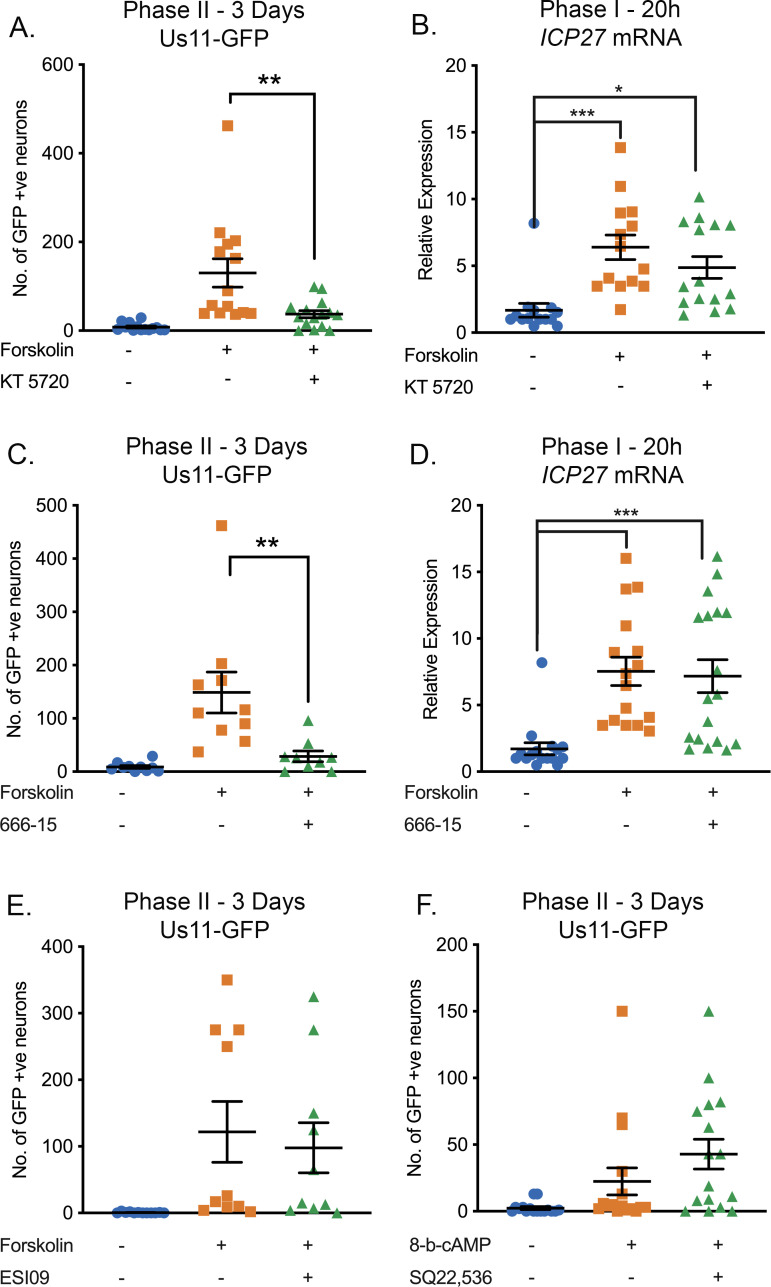
Figure 2. Reactivation triggered by forskolin involves a DLK/JNK-dependent phase I of viral gene expression.
(A) Reactivation was induced by forskolin in the presence of JNK inhibitor SP600125 (20 μM). (B) Reactivation was induced by forskolin in the presence of the DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM). In A and B each experimental replicate is shown. (C) Reactivation was induced by forskolin or superinfection with a wild-type (F strain) HSV-1 (MOI of 10 PFU/cell) and qualified based on Us11-GFP-positive neurons (n = 3). (D–F) RT-qPCR for viral mRNA transcripts following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs. (G–I) RT-qPCR for viral lytic transcripts at 20 hr post-forskolin treatment and in presence of the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (20 μM) and the DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 (4 μM). (J) Neurons were transduced with a non-targeting shRNA control lentivirus or two independent lentiviruses expressing shRNAs that target DLK (shDLK-1, shDLK-2). Western-blotting for DLK or β-III tubulin was carried out 3 days post transduction. The percentage knock-down of DLK normalized to β-III tubulin is shown. (K and L) RT-qPCR for viral mRNA transcripts following forskolin treatment of latently infected SCGs that were either transduced with the shRNA control or shRNA DLK lentiviruses. In D-I, K, and L, each experimental replicate is represented. Statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. The mean and SEM are shown.