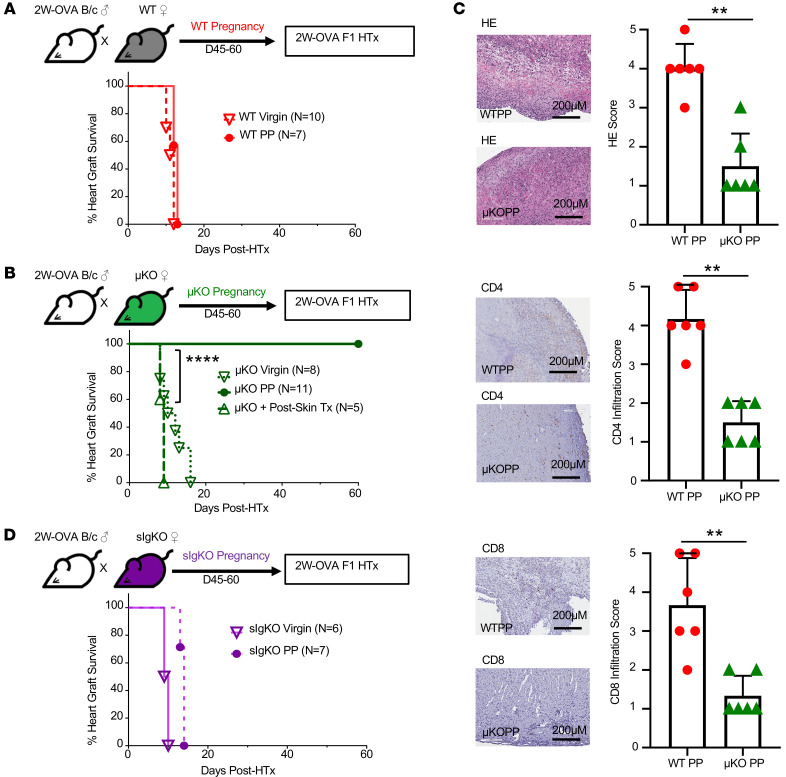
Figure 4. In the absence of B cells, allogeneic pregnancy induces spontaneous F1 heart graft acceptance.
(A) Experimental design. Male 2W-OVA.BALB/c were mated with C57BL/6. After resting for 45–60 days, WT PP females were transplanted with 2W-OVA.F1 hearts without tolerance induction. Percentage of heart graft survival, virgin vs. PP WT; n = 7–10/group. (B) Experimental design. Male 2W-OVA.BALB/c mated with μKO.C57BL/6. μKO PP mice were rested for 45–60 days and then transplanted with 2W-OVA.F1 hearts without tolerance induction. Percentage of heart graft survival; n = 5–11/group, virgin μKO vs. PP μKO; ****P < 0.0001, log-rank test. (C) Histology of allograft for WT PP and μKO PP analyzed at day POD60 or later. Histology scores were based on abnormalities, decellularization, and cell infiltration for H&E stain and IHC staining for CD4+ and CD8+ cells. n = 6/group. Original magnification, ×20. Scale bars: 200 μm. (D) Experimental design. Male 2W-OVA.BALB/c were mated with sIgKO.BL/6. After resting 45–60 days, PP sIgKO females were transplanted with 2W-OVA.F1 hearts without tolerance induction. Percentage of heart graft survival; n = 6–7/group. Data are pooled from 2 independent experiments and represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney t test. Heart graft survival data in virgin WT, μKO, and sIgKO mice are from Figure 2C and Figure 3, C and F, respectively.