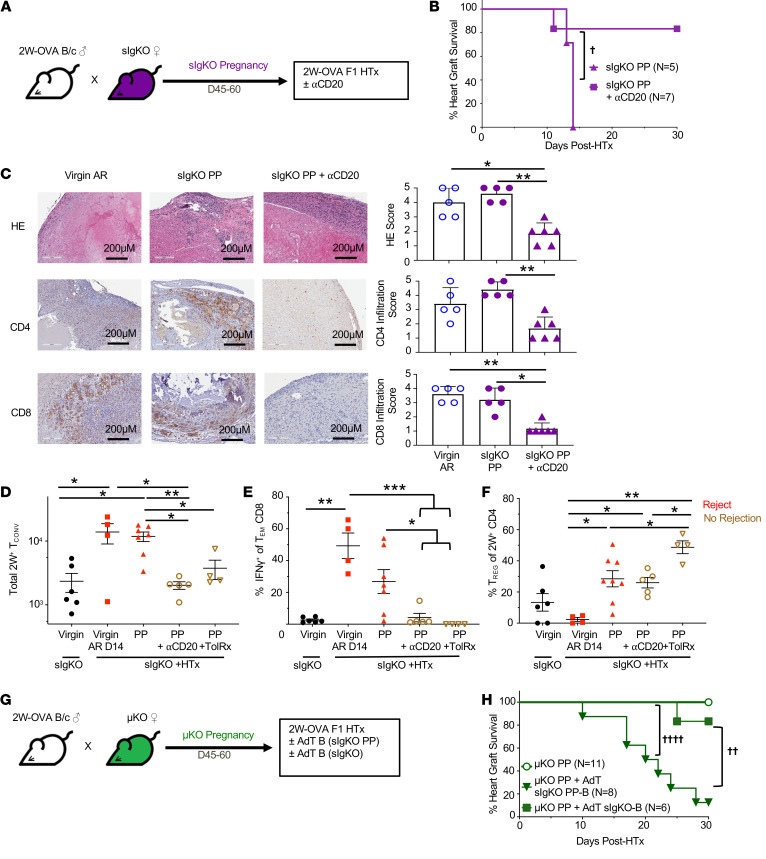
Figure 5. Pregnancy-sensitized B cells at the time of HTx overrides pregnancy-induced T cell tolerance.
(A) Experimental design. Male 2W-OVA.BALB/c were mated with female sIgKO.BL/6. After resting 45–60 days, sIgKO PP females received 250 μg anti-CD20 antibody (i.v.) on days –1 and 7 after 2W-OVA.F1 HTx. (B) Percentage of heart graft survival; n = 5–7/group. †P < 0.05, log rank test. (C) Histology of allograft for virgin acute rejection (AR), PP sIgKO, and PP sIgKO with anti-CD20 analyzed at POD30 or later. Graft scores were determined based on abnormalities, decellularization, and infiltration for H&E stain and IHC for infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ cells; n = 5–6/group. Original magnification, ×20. Scale bars: 200 μm. Spleens and inguinal, axillary, and brachial LN were harvested from indicated mice, and PP +HTx recipients were examined on day 30 after HTx. (D) Total number of 2W+ Tconvs; n = 4–7/group. (E) Percentage of IFN-γ+ of Tem CD8+ cells; n = 4–7 group. (F) Percentage of Tregs of 2W+ CD4+ cells; n = 4–8/group. (G) Experimental design. Male 2W-OVA.BALB/c were mated with female μKO.C57BL/6. After resting for 45–60 days, μKO PP females were transplanted with 2W-OVA.F1 heart graft with or without adoptive transfer of B cells purified from sIgKO PP or virgin sIgKO 1 day prior to heart transplantation. (H) Percentage of heart graft survival; n = 6–11/group. ††P < 0.01; ††††P < 0.0001, log-rank test. Heart graft survival data for sIgKO PP and μKO PP mice are from Figure 4, D and B, respectively. All data are pooled from 2 independent experiments and represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc