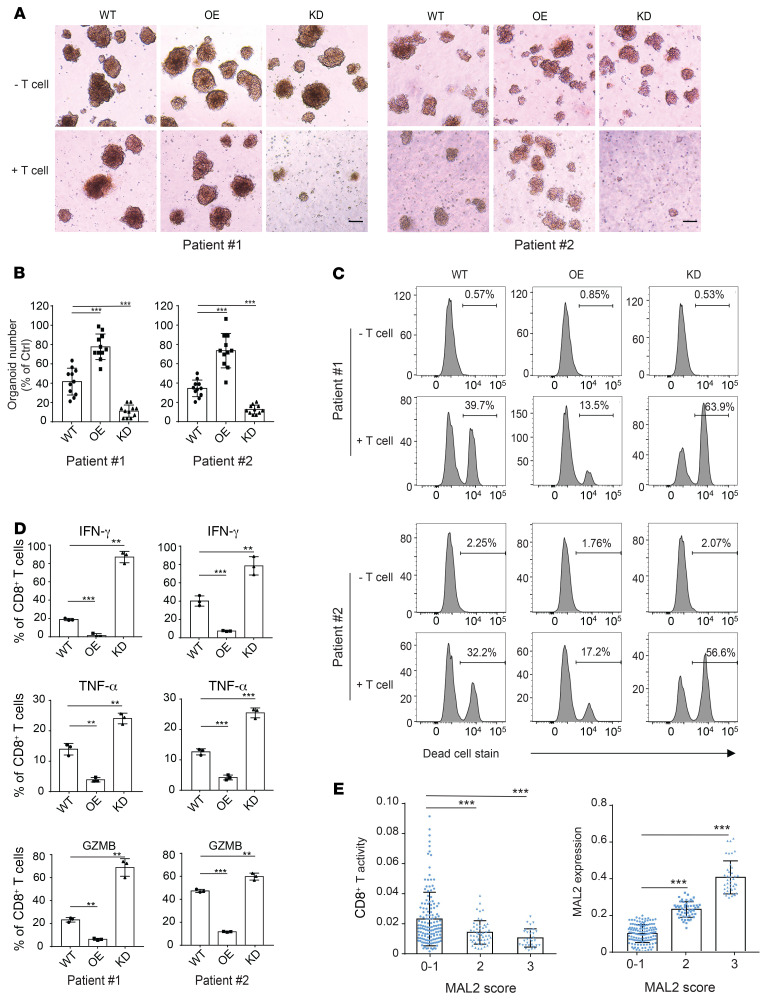
Figure 9. Depletion of MAL2 enhances CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity in human TNBC tumors.
(A) MAL2 levels in tumor cells affect the cytotoxicity of the tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in human TNBC tumors. Tumor cells isolated from fresh TNBC tumor tissues (patient #1 and #2) were transduced with lentiviral MAL2 or its shRNA. The tumor cells formed spheroids with CAFs isolated from the same tumor tissue. The tumor spheroids were cocultured with preactivated CD8+ T cell isolated from the same tumor tissue to detect the T cell cytotoxicity (spheroid dissociation rates). Representative images of spheroids are shown. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Quantitative data are presented as mean ± SD of represented images from 3 parallel experiments in A. (C) Spheroids from A were digested into single cells, which were stained for EpCAM (tumor cells), anti-CD140a (CAFs), and LIVE/DEAD dead-cell stain. Flow cytometry data show the CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity in patient-derived CAF-tumor spheroids with different MAL2 expression levels. (D) The CD8+T cells collected from A were analyzed for their activity. The CD8+ T cells were incubated with 50 ng/mL PMA, 1 μg/mL ionomycin, and 5 μg/mL brefeldin A for 5 hours, and were stained with antibodies against IFN-γ, TNF-α, and GZMB. Quantitative data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 technical experiments. (E) Correlation of MAL2 levels (pathological scores) with tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity (determined by GZMB levels) in human breast tumor tissue microarrays. Immunohistochemical analyses of MAL2, CD8, and GZMB in human TNBC TMA slides were conducted, and quantitative results were obtained as described in Supplemental Methods. Statistical analyses were conducted using 1-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.