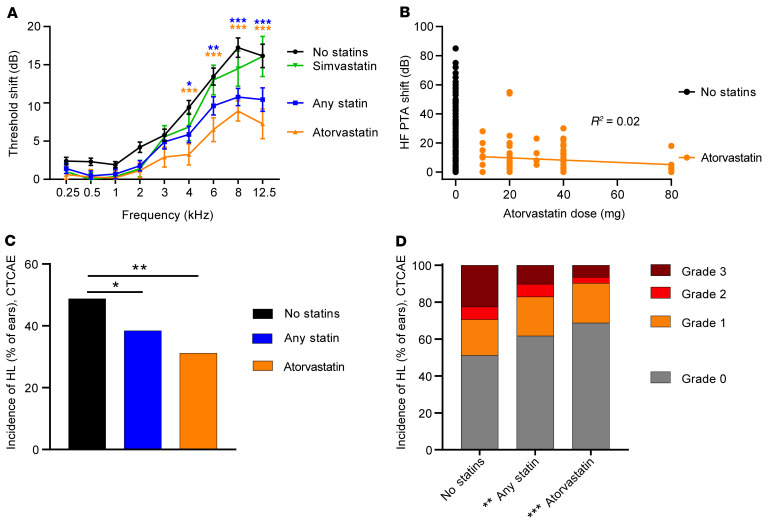
Figure 2. Atorvastatin use is associated with reduced cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
Baseline audiometric thresholds were compared with thresholds obtained after cisplatin treatment to determine threshold shifts. (A) In subjects not taking a statin (N = 324 ears), cisplatin treatment resulted in threshold shifts that were more severe at higher frequencies. Subjects taking any statin (N = 219 ears) had significantly less cisplatin-induced hearing loss than subjects who were not taking a statin. Atorvastatin users (N = 97 ears) had significantly less cisplatin-induced hearing loss than nonstatin users. In contrast, cisplatin-induced threshold shifts among simvastatin users (N = 70 ears) were not significantly different from those of nonstatin users. Data represent mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. (B) Atorvastatin dose was not correlated with high-frequency (6–12.5 kHz) hearing loss. Each dot represents 1 ear. Nonstatin users (N = 324 ears) had 15.9 ± 20.3 dB shifts in high-frequency pure tone average (HF PTA). Atorvastatin users (N = 97 ears) had shifts of 7.8 ± 11.8 dB. There was no correlation between atorvastatin dose and threshold shift. Pearson R correlation. (C) The incidence of cisplatin-induced hearing loss among nonstatin users was 48% per CTCAE criteria. Subjects taking any statin had significantly lower incidence of hearing loss than nonstatin users. The incidence of hearing loss was further reduced among atorvastatin users. Data are percentage of ears per group. Statistical analysis consisted of the χ2 test. (D) Statin use, atorvastatin in particular, was associated with reduced severity of hearing loss. CTCAE criteria were used to categorize the severity of hearing loss. χ2 Analysis showed a significant difference in the distribution of CTCAE hearing loss grades, where the incidence of a grade 2 or higher hearing loss was reduced in statin users compared with nonstatin users. This difference was even greater for atorvastatin users. Data are percentage of ears per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.