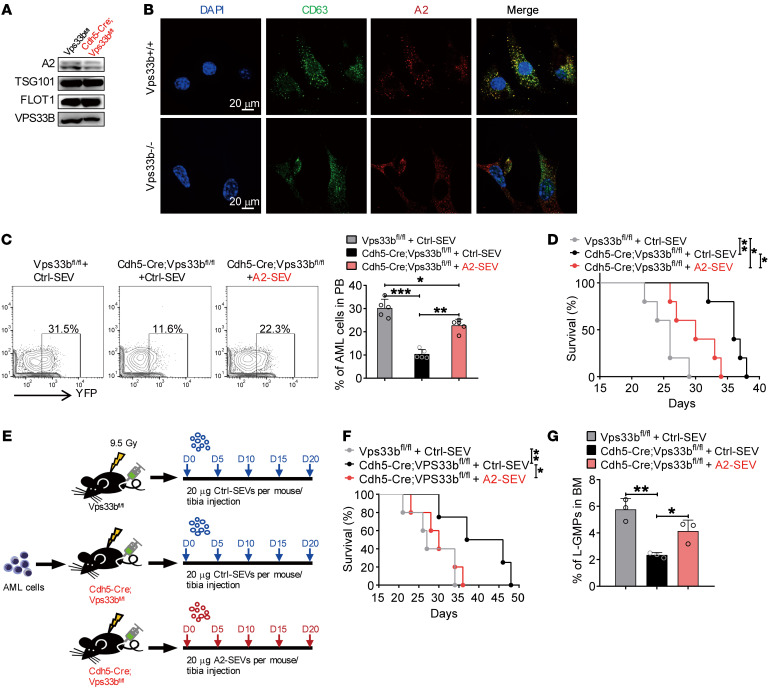
Figure 7. VPS33B regulates ANGPTL2-SEV release.
(A) Western blot analysis of ANGPTL2, TSG101, FLOT1, and VPS33B protein levels in BM fluid SEVs from Vps33bfl/fl mice and Cdh5-Cre;Vps33bfl/fl mice. (B) Colocalization of CD63 and ANGPTL2 in WT and VPS33B-null ECs. (C) Flow cytometry (left) and histogram (right) analysis of the percentages of YFP+ AML cells in the PB of the indicated recipients injected with AML cells cocultured with Ctrl-SEVs or ANGPTL2-SEVs (n = 5; the data represent the means ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test). (D) Survival analysis of the indicated recipients injected with AML cells cocultured with Ctrl-SEVs or ANGPTL2-SEVs (3 μg per 1 × 105 AML cells) (n = 5; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, log-rank test). (E) The in vivo administration of ANGPTL2-SEVs into Cdh5-Cre;Vps33bfl/fl mice and Vps33bfl/fl control recipients. Equal volumes of Ctrl- or ANGPTL2-SEVs (20 μg) were intratibially injected every 5 days for 20 days. (F) Survival analysis of AML recipients injected with Ctrl- or ANGPTL2-SEVs (n = 5; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, log-rank test). (G) The percentage of L-GMP cells in BM of indicated recipients (n = 5; the data represent the means ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test). Experiments were conducted 2 times for validation.