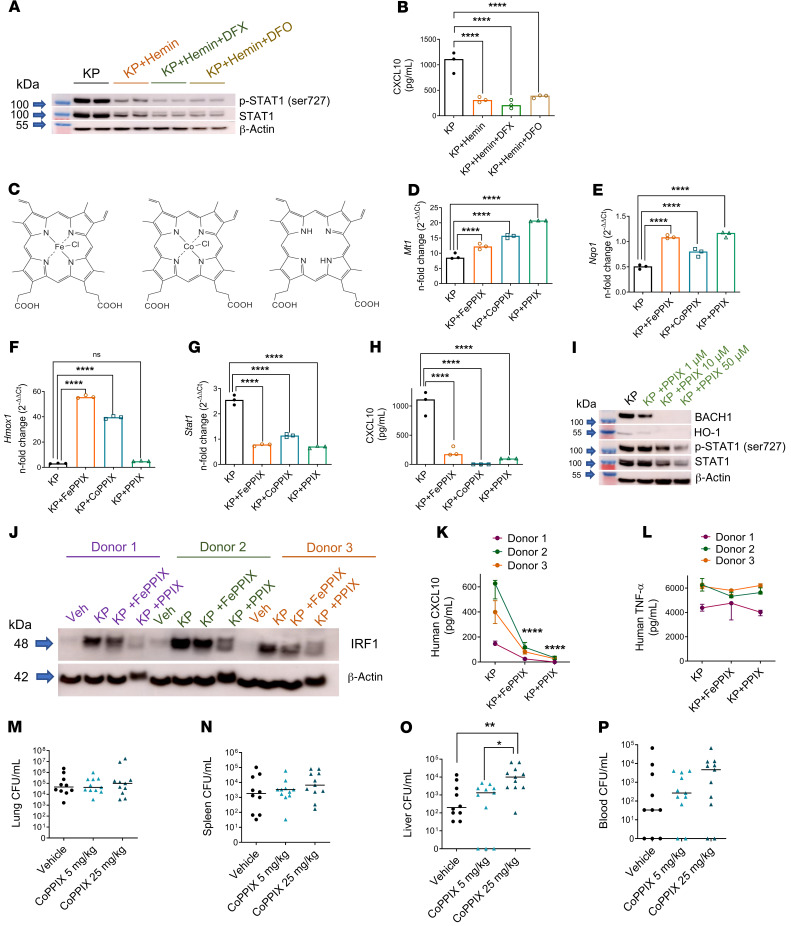
Figure 7. The porphyrin moiety of heme is necessary and sufficient for NRF1/NRF2 activation and STAT1 suppression.
(A) STAT1 immunoblot in BMDMs challenged with KP (MOI 10:1), KP + hemin (25 μM), KP + hemin + DFX (300 μM), or KP + hemin + DFO (300 μM) for 4 hours. All groups contained vehicle (DMSO, ~1%). Blot is representative of 2 independent experiments. (B) CXCL10 was measured in cell culture supernatant by ELISA 4 hours after infection. (C) Chemical structures of hemin (iron protoporphyrin IX, FePPIX), cobalt protoporphyrin IX (CoPPIX), and protoporphyrin IX (PPIX). (D) Mt1 and (E) Nqo1 expression, (F) Hmox1, and (G) Stat1 gene expression, (H) CXCL10 secretion in BMDMs challenged with KP, KP + FePPIX (50 μM), KP + CoPPIX (50 μM), or KP + PPIX (50 μM) for 4 hours. (D–G) Fold change relative to PBS-treated BMDMs. (B and F–H) n = 3 technical replicates per group. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (I) BACH1, HO-1, p-STAT1, and total STAT1 immunoblot in BMDMs challenged with KP and increasing concentrations of PPIX. (J) IRF1 immunoblot in human monocyte–derived macrophages (HMDMs) challenged with vehicle (PBS), KP, KP + FePPIX (25 μM), or KP + PPIX (25 μM) for 4 hours. (K) CXCL10 and (L) TNF-α secretion from HMDMs in J. n = 3 donors. ****P < 0.0001 by 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. KP was instilled intratracheally into C57BL/6 mice and followed by i.p. challenge with vehicle (2.5% DMSO) or CoPPIX (5 mg/kg, 25 mg/kg) 1 hour after KP instillation. Bacterial burden was obtained from (M) lung, (N) spleen, (O) liver tissue homogenates, and (P) blood of mice 24 hours after KP infection and reported as CFU/mL. Each point indicates individual mice, n = 10–11 mice per group combined from 2 independent studies. Line indicates median. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test.