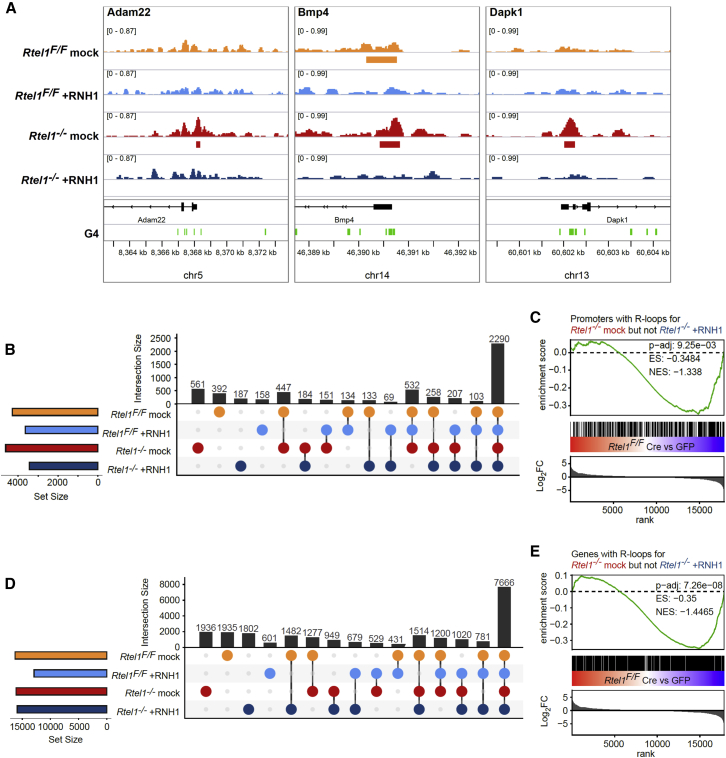
Figure 5.
Rtel1−/−-Induced R-Loops Are Related to Rtel1−/−-Induced Transcriptional Changes
(A) Rtel1F/F;WT RNH1-GFP MEFs were infected with GFP or Cre-GFP adenovirus. After 48 h, doxycycline was added, and cells were collected after 48 h and used for R-loop detection with DRIP-seq. Genome browser plots of normalized read coverage, called peaks of DRIP-seq, and associated predicted G4 structures in three different genomic locations.
(B) Overlap analysis of DRIP-seq peaks in promoters. Upset plot that depicts the numbers of promoters with R-loops shared between Rtel1F/F and Rtel1−/−, dependent on RNaseH1.
(C) GSEA that shows transcriptional enrichment of genes with Rtel1−/−-specific and RNH1-sensitive promoter R-loops. Genes are ranked dependent of Log2FC of differential expression with deleted Rtel1 (Rtel1F/F, Cre versus GFP). The overall ES and NES with the respective pvals were determined of the enrichment with R-loop peaks that are present with Rtel1 deletion, yet not present with RNaseH1 overexpression.
(D) Overlap analysis of DRIP-seq peaks in genes. Upset plot that depicts the numbers of genes with R-loops shared between Rtel1F/F and Rtel1−/−, dependent on RNaseH1.
(E) GSEA that shows transcriptional enrichment of genes with Rtel1−/−-specific and RNaseH1-sensitive R-loops. Genes are ranked dependent of Log2FC of differential expression with deleted Rtel1 (Rtel1F/F, Cre versus GFP). The overall ES and NES with the respective pvals were determined of the enrichment with R-loop peaks that are present with Rtel1 deletion, yet not present with RNaseH1 overexpression.