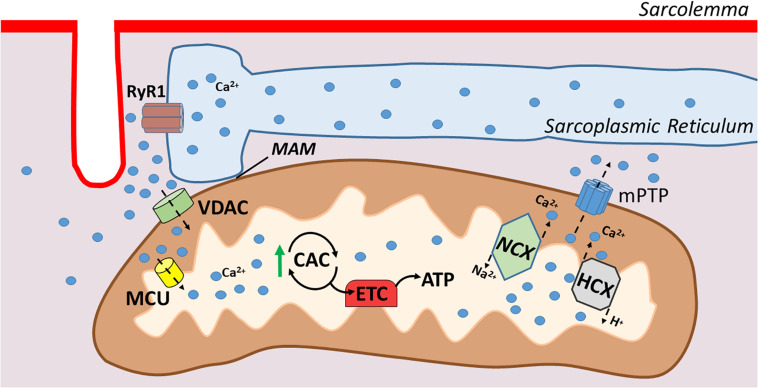
FIGURE 2.
Illustration of mitochondrial calcium transport. Mitochondrial associated membranes (MAMs) result in microdomains of high Ca2+ levels that facilitate Ca2+ entry through the outer mitochondrial membrane via voltage dependent anion channel (VDAC). Ca2+ crosses the inner mitochondrial membrane via the mitochondrial uniporter (MCU), which then stimulates respiration via increases in citric acid cycle enzymes. Ca2+ is extruded from the mitochondria via Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) and H+/Ca2+ exchanger (HCX) in the inner membrane and the outer membrane via the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP).