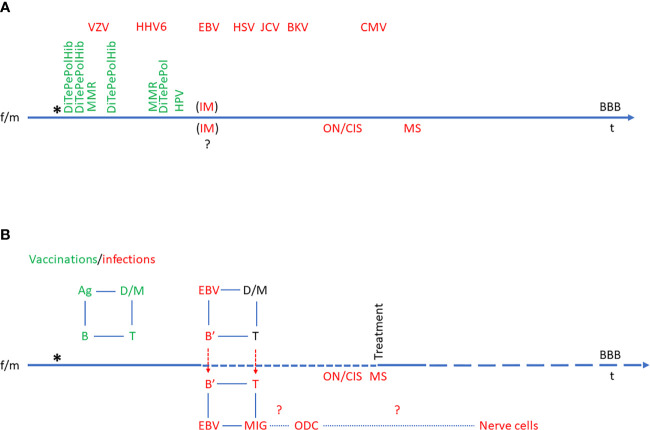
Figure 1.
Model of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)’s role in multiple sclerosis (MS). The time line also represents the blood-brain-barrier (BBB) and events across the BBB. The birth of a child subsequent to the mixing of a female (f) and a male (m) set of genes is indicated by an asterisk (*). (A) Time course of normal immune system development with vaccinations (green) and infections (red). The order and time course of vaccinations is defined by vaccination regimens. The order of infections is individual and variable, so the sequence indicated is hypothetical. In some individuals, EBV infection may manifest itself as IM, and it is not known to which extent infectious mononucleosis (IM) affects the CNS at the time of primary infection, but it is known to increase the risk of ON/CIS and eventually MS. (B) Schematic presentation of etiological immunological reactions in multiple sclerosis in relation to vaccinations and infections. The normal immunological feed-back loop is indicated in green (e.g., vaccination-induced Ag uptake by dendritic cells (D) and macrophages (M), which interact with T cells, which in turn interact with B cells and vice versa). In the case of EBV infection, the immunological feed-back loop is re-programmed to the advantage of EBV, resulting in chronic infection of B cells (B’). These may enter the CNS (particularly in the case of IM) and be followed by T cells. This results in inflammation in the CNS with the feed-back loop also involving microglia cells (MIG) and at some point also oligodendrocytes (ODC) and eventually, nerve cells. Ag, antigen; B, B cell; B’, EBV-infected B cell; BBB, blood-brain barrier; BKV, B. K. Virus infection; CIS, clinically isolated syndrome; CMV, Cytomegalovirus infection; D, dendritic cell; DiTePePolHib, Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis-Polio-Hemophilus influenzae B vaccine; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus infection; f, female; HHV6, Human Herpes Virus 6 infection; HPV, Human Papilloma Virus vaccine; HSV, Herpes Simplex Virus infection; JCV, John Cunningham Virus infection; IM, infectious mononucleosis; m, male; M, macrophage; MIG, microglia cell; MMR, Measles-Mumps-Rubella vaccine; MS, multiple sclerosis; ODC, oligodendrocyte; ON, optic neuritis; t, time; T, T cell; VZV, Varicella Zoster Virus infection.